China Cloud Computing: Q3 2022 Review
Listen
China’s cloud computing and software sector has not been immune to the challenging global and domestic macro environment, experiencing a late-cycle slowdown over 3Q22. A confluence of economic and Covid-related impacts has meant both governments and enterprises are delaying their IT budget spending, even as their longer-term demand for cloud-based digital transformation and software localization remains intact. For investors, we believe this presents potential upside opportunities once macroeconomic conditions improve and focus on digital transformation returns.
Key Takeaways
- China’s cloud computing sector is seeing a divergence among different service providers. Large internet players have experienced a slowdown in cloud revenue growth this year, while telecom operators providing hardware and private cloud solutions showed strong growth momentum. Despite near-term uncertainties amid a slowing macro environment, we believe the cloud market will continue to develop rapidly over the medium to longer term.
- On the software side, revenue growth remains weak, reflecting the late-cycle nature of the industry. Private enterprises more vulnerable to economic downturns have seen greater pullbacks in IT spending. However, we expect activity to pick up once the macro environment improves, especially as software localization remains a big trend.
Cloud Computing: Divergent Performance
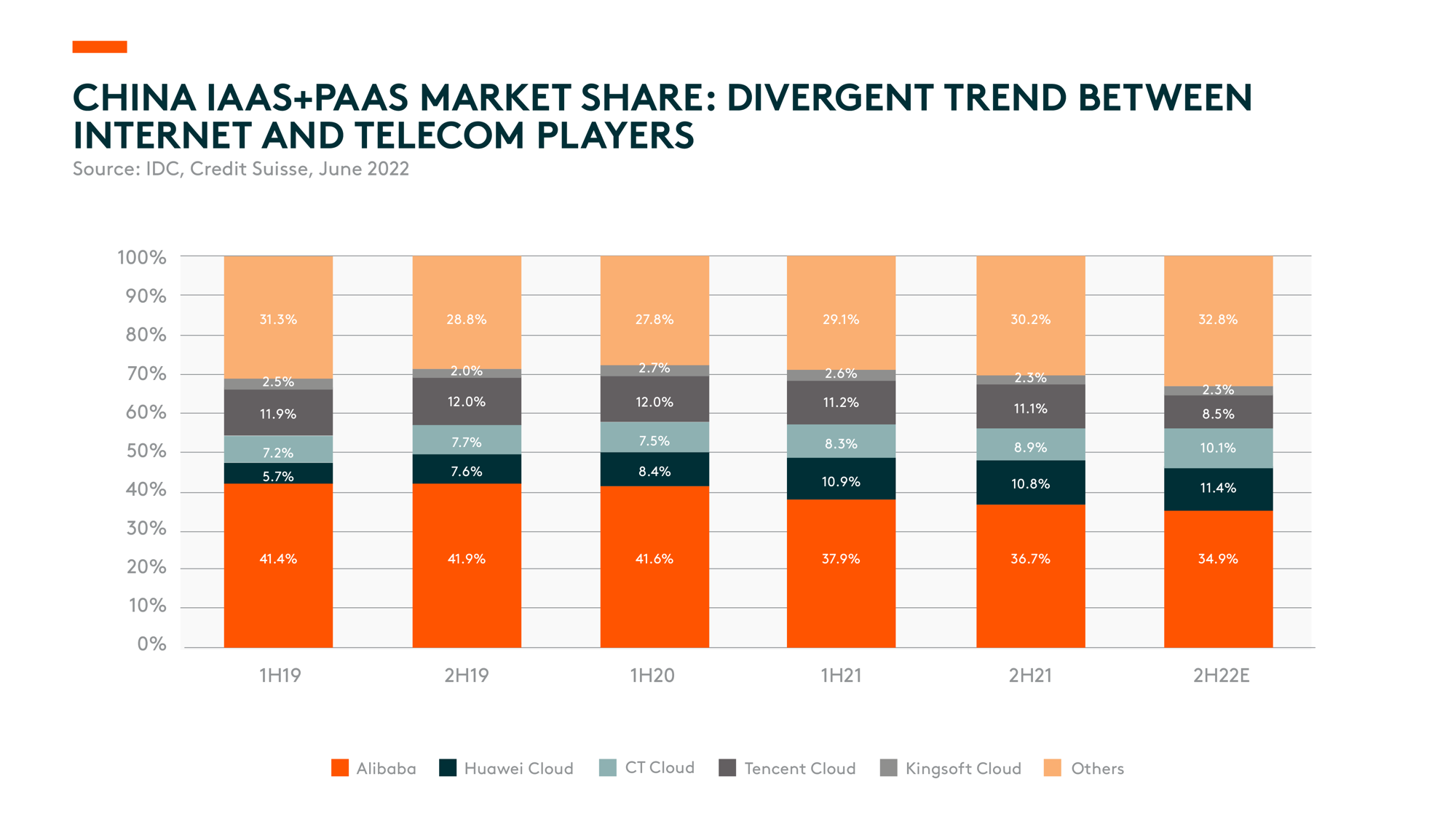
China’s cloud computing sector is seeing a divergent performance by different service providers. On the one hand, internet players like Alibaba, Tencent, and Baidu have decelerated cloud revenue growth over the past few quarters, mainly due to reduced spending from internet customers. The global chipset shortage disrupted supply chains, while China’s Covid-19 resurgence and lockdown measures disrupted rack servers and rack-scale systems manufacturing. Public cloud services providers are now shifting focus from IaaS (Infrastructure-as-a-Service), especially low-margin/low value-add projects, to PaaS (Platform-as-a-Service). The PaaS products released by public cloud services companies tend to provide module-based solutions and reduce the total coding workload required to develop software applications. Although current revenue contribution from PaaS remains minor, relevant products have proven strong value propositions for individual software developers and small enterprises.
On the other hand, policy and regulatory requirements have tightened for the government and financial sectors in recent years, and certain business applications have been gradually migrated back to the private cloud. In addition, deployment in other industries is more likely concerned with data security and business confidentiality. This has led to the growing momentum of private and hybrid cloud demand, especially for state-owned enterprise (SOE) customers, given they’re primarily in financial or manufacturing industries with higher data security requirements. As a result, the telecom operators’ (China Telecom and China Mobile) cloud businesses, which cover more hardware sales and private cloud solutions, reported more than 100% year-on-year growth for the past quarter, showing strong upward momentum.
Although Covid has impacted demand for cloud computing in the short term, cloud-based digital transformation has become a primary catalyst for enterprises to accelerate their development and adopt the macro environment. As a result, we expect the cloud market to continue to develop rapidly.
Software: Weak Industry Revenue Growth
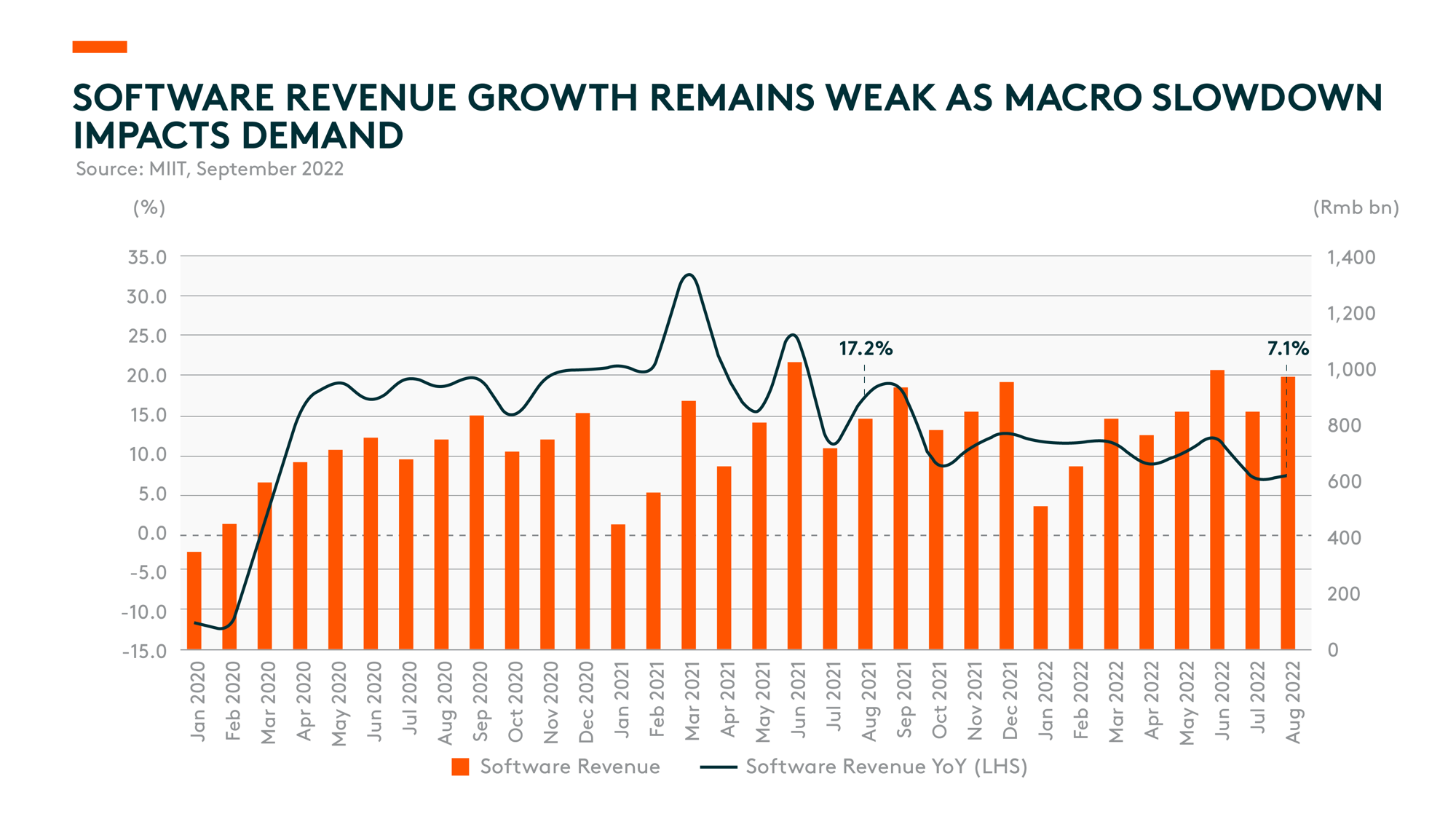
For software, overall industry revenue growth remained weak for 3Q22. According to MIIT, August software and IT services revenue grew only 7.1% year-on-year, the same as July and even weaker than 2Q, when multiple cities experienced extensive lockdowns, severely impacting client onboarding and project implementation. This reflects the overall late-cycle nature of the software industry, as sustained weak customer IT spending amid a slow macro recovery continues to impact demand.
By customer type, private enterprises show higher vulnerability to macro downturns and reduced spending on software. As a result, we’re seeing decelerated revenue growth and downward margin revisions for many vertical software companies, especially those exposed to real estate (due to policy tightening on property development) and consumer retailing. However, demand for smart auto software is particularly strong, attributable to the growing penetration of electric vehicles (EVs) and the increasing value of intelligent software within the automotive supply chain. Government IT spending is also sluggish, as local governments prioritize their budgets on Covid-19 testing and controls, and stimulating housing demand and consumption.
In our view, these IT spends will be delayed rather than diminished. Both enterprises and government organizations can experience strong efficiency gains and operational streamlining through digital transformation. Therefore, we believe this trend will pick up again once the macroeconomic condition improves.
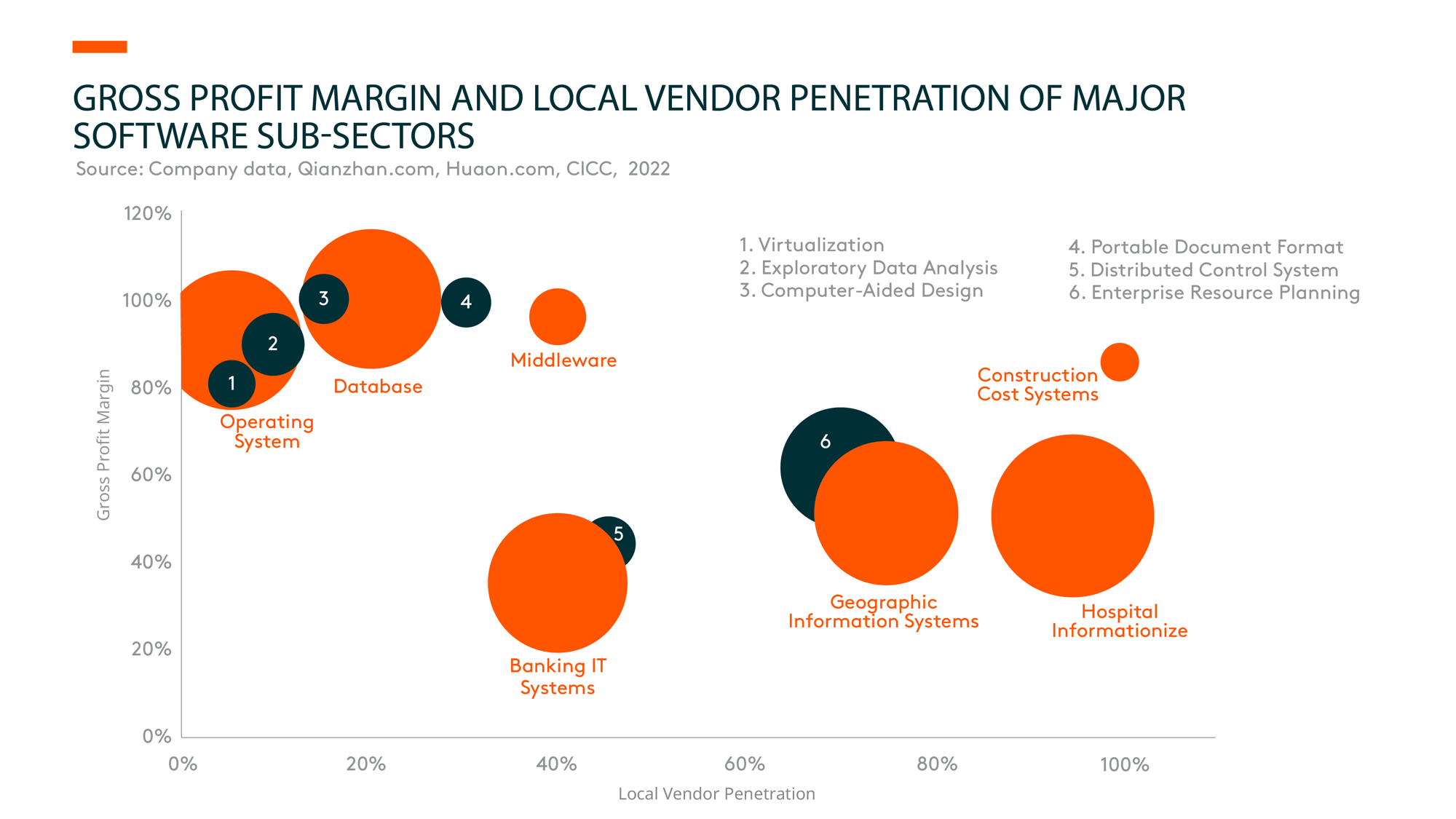
Software localization remains a key trend, given the rising geopolitical tensions between US and China. There’s still a gap (such as in technology capability and software performance stability) between domestic and foreign vendors in sub-sectors like basic software (operating systems, middleware, and database), industrial software, high-end enterprise resource planning (ERP), etc. However, local software companies have accelerated their investments in research and development (R&D), despite continuous pressure on top-line growth amid a fluid macro situation. While this has led to declining margins for many, it’s also supported the rising penetration of local software products in many verticals.
Finally, as copyright becomes a growing emphasis, the emergence of local suppliers is lowering clients’ burden when transforming to paid users. This should drive the usage of authorized software and offer significant monetization opportunities for local software companies. Domestic companies are also enhancing their software functions, and user interface, and adding more industry modules to enhance the price-to-performance ratio to attract clients.