Chinese Vaccine Industry Research Series II – Vaccine Front-runners Head Toward the Finish Line
In our previous series ‘Vaccines: Past, Present, and Future,’ we discussed the overview and types of vaccines. In this edition, we explore different types of vaccines for COVID-19, the manufacturing companies, and the development status and timelines.
Broadly, there are two categories of COVID-19 vaccine in development –
- Traditional vaccines – e.g., recombinant protein, inactivated/live attenuated virus, and adenovirus vector vaccines that consist of either a viral protein or virus-like particle. They form the basis of established vaccines industry and all approved vaccines (made by Sanofi, GSK, Merck, Pfizer, and JNJ).
- Novel vaccines – e.g., mRNA, DNA vaccines such as Moderna’s (the first to enter clinical trials), Sanofi/TranslateBio’s or Pfizer/BioNtech’s that only comprises of the viral genetic material. Once introduced into the body, the body’s cells manufacture virus antigens prompting an immune response.
Traditional Vaccines – Easier and faster to get approval
The advantages of traditional vaccines include the ease of obtaining regulatory approval on an accelerated timeline given higher regulatory comfort with established technologies and established manufacturing. However, this may be more difficult/slower to scale up to the billions of doses potentially needed. Per Sanofi management, it has developed a vaccine based on the previous severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) vaccine by its traditional recombinant DNA (encoding COVID-19 spike protein) technology. More importantly, it would be able to obtain approval 12-18 months from now with a manufacturing capacity of 100-600mm doses. It will use existing cell-based manufacturing that it uses for its annual Flublok flu vaccine. We believe it may be conservative following its subsequent tie-up to use GSK’s adjuvant. Similarly, JNJ announced that it anticipates the first batch of its adenovirus vector vaccine could be available for emergency use by early 2021, a substantial acceleration versus typical vaccine timelines. Capacity expansion is planned to be able to supply 1 billion doses.
Novel Vaccines – Unproven, faster development speed, manufacturing scale-up easier than tradition vaccines
The development speed with viral genome sequencing to the production of a candidate vaccine for testing has been achieved in a matter of weeks, by Moderna as well as Pfizer/ BioNtech. This has allowed mRNA vaccine development companies to enter clinical trials earlier (vs. 2H20 expected for traditional vaccines). Potential for fast simpler/cheaper manufacturing scale up with large-scale nucleic acid manufacturing appears to be easier than protein manufacturing required for conventional vaccines. However, novel RNA/DNA vaccines are also unproven, higher-risk, and likely more tricky and potentially slower to attain approval.
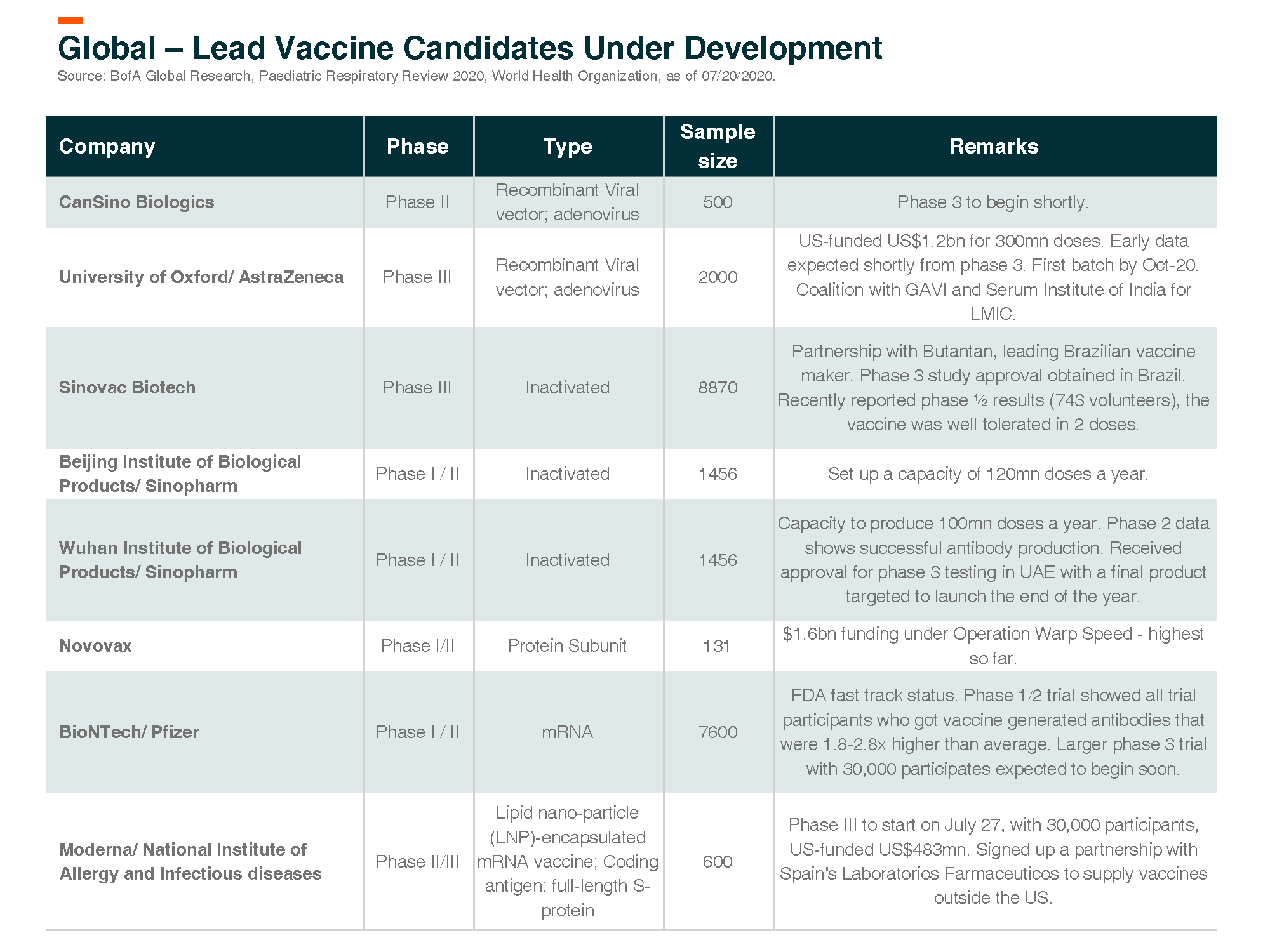
Globally about 160 vaccine programs for COVID, 23 in clinics
According to WHO, about 160 active vaccine development programs are for COVID, 23, and about 140 are in clinical and pre-clinical stages.
Below we discuss vaccine updates for specific leading companies.
Moderna – Leader of mRNA Vaccine
Moderna’s Phase I COVID-19 vaccine mRNA-1273 was published in the NEJM (patient size = 45). It demonstrated positive efficacy and safety data. The data on neutralizing antibody levels are 2-4x greater than convalescent sera, which is at least as good as recently reported and well-regarded positive data from PFE/BNTX that was 2-3x fold greater. Other details are important and positive as well, including activation of T-cell responses, which are important in fighting off infection and increasing durability. Plans to commence phase III trials (with 30k participants) is expected to take place soon. Moderna has received US$483mn from the US government as funding to accelerate the development of the vaccine.
Cansino – Phase 1 data encouraging, phase 3 trial to begin soon
Cansino’s vaccine candidate Ad5-nCoV – China PhI results show initial signs of immunogenicity with manageable safety profiles. In terms of immunogenicity, Ad5-nCoV induced humoral and T-cell responses were rapid in most subjects. 50-75% of subjects had four-fold increases in neutralizing antibodies (NAb). The company plans to expand capacity to 100-200mn doses (including overseas partners).
Canada update – Health Canada has reviewed Cansino’s pre-clinical and clinical data in China and has approved to commence clinical trial in Canada.
mRNA partnership – Cansino has also entered into a joint-venture (JV) with Precision NanoSystems (PNI) to co-develop its mRNA lipid nano-particle (mRNA-LNP) vaccine against COVID-19. The JV will leverage PNI’s proprietary RNA vaccine platform, comprising of lipid nano-particle delivery system and the manufacturing technology, to advance its COVID-19 mRNA-LNP vaccine candidate.
Serum Institute of India
India produces 60% of the world’s vaccines and accounts for 60%-80% of the United Nations’ annual vaccine procurement. 107 of total 153 WHO pre-qualified vaccines are from India. Among Indian firms, Serum Institute, Bharat Biotech, Panacea Biotech, Cadila Healthcare, and Indian Immunological are leading vaccine players.
Serum Institute is the world’s largest vaccine maker by number of doses (1.5bn annually) produced and sold in more than 170 countries. Serum has collaborated with the University of Oxford (and now licensed to AstraZeneca) for a vaccine for COVID-19. The vaccine is currently in phase II/ III clinical trial. Serum will manufacture and supply the vaccine. As per its agreement with AstraZeneca, Serum is to provide 1 billion doses to low-and-middle-income countries, with 400 million of those shots set to be delivered by the end of 2020.
Related ETF
Global X China Biotech ETF seeks to provide investment results that closely correspond to the performance of the Solactive China Biotech Index NTR, offering an access high growth potential through companies critical to the development of biotechnology in China.
Other Features
Targeted Exposure: The fund delivers targeted exposure to an emerging theme and industry.
ETF Efficiency: In a single trade, the fund delivers access to dozens of companies with high exposure to the biotech theme in China.
Click here to learn more about our Global X China Biotech ETF.