China Robotics & AI Industry: H1 2022 Review
Supply chain tightness remains the key buzzword affecting all automation and robotics companies during H1 22. The ability to manage supply chains whilst being agile was critical for manufacturers during the China lockdown. We continue to believe that Chinese players who are able to demonstrate strong management of local supply chains are likely to gain further market share during such periods of disruption.
Automation Demand Varied Across Verticals During the Pandemic Lockdown
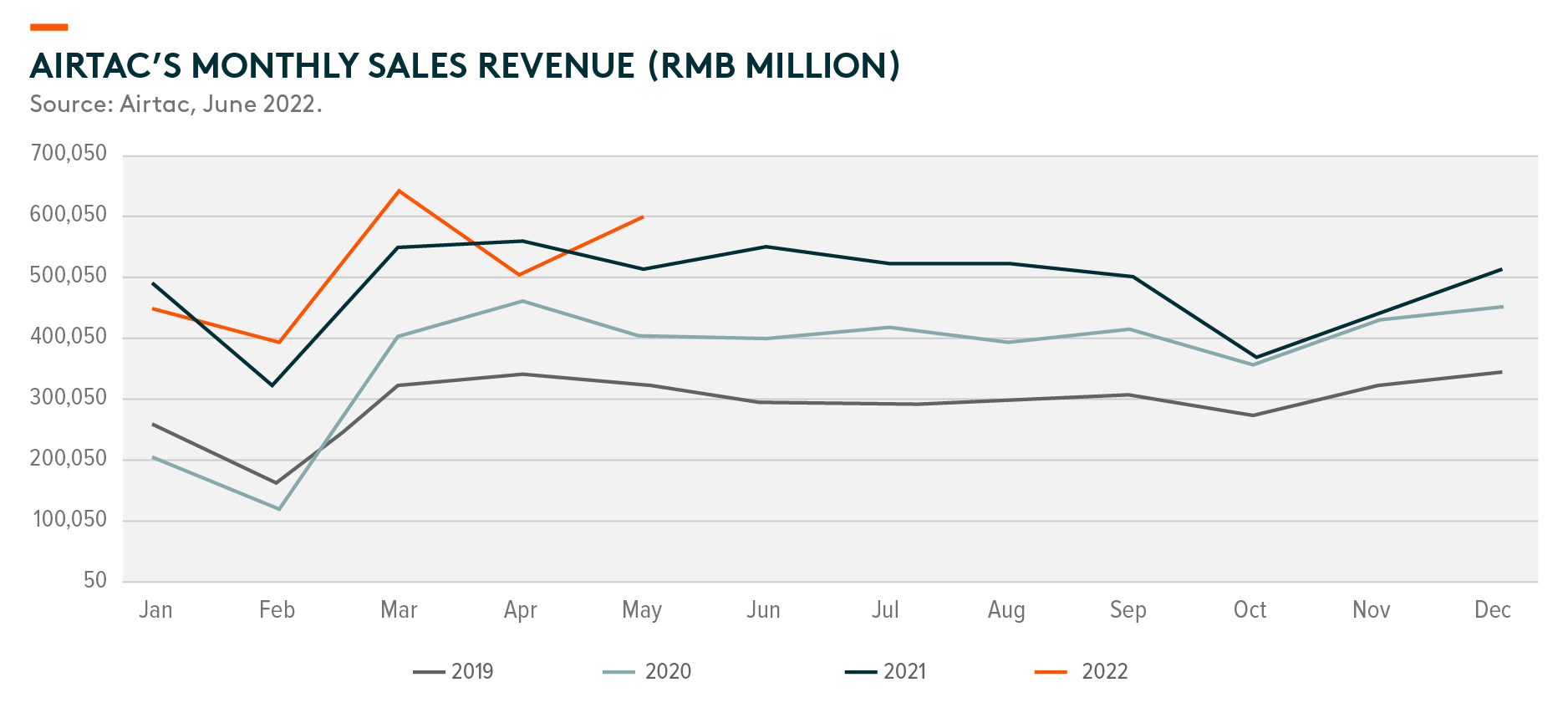
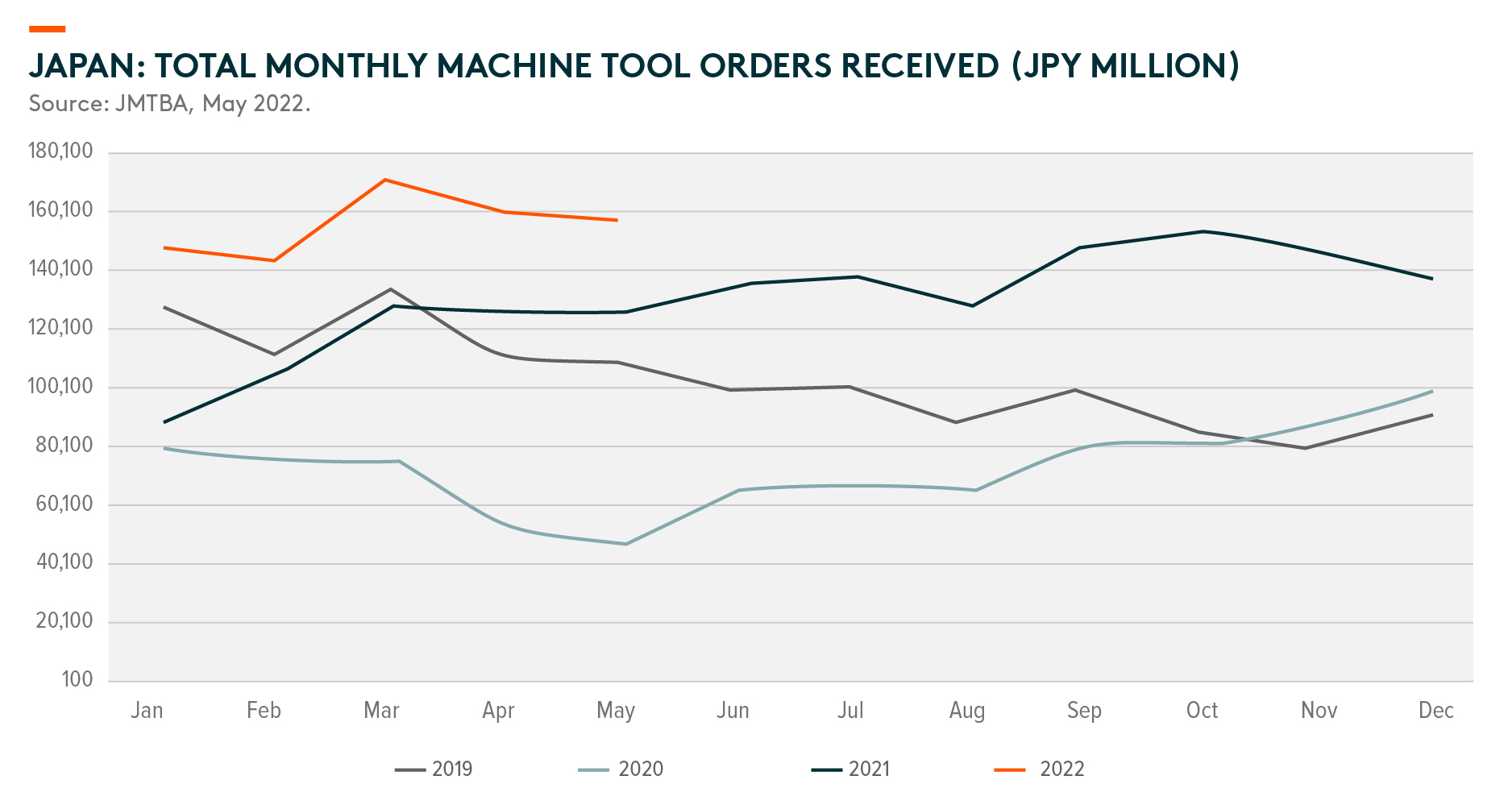
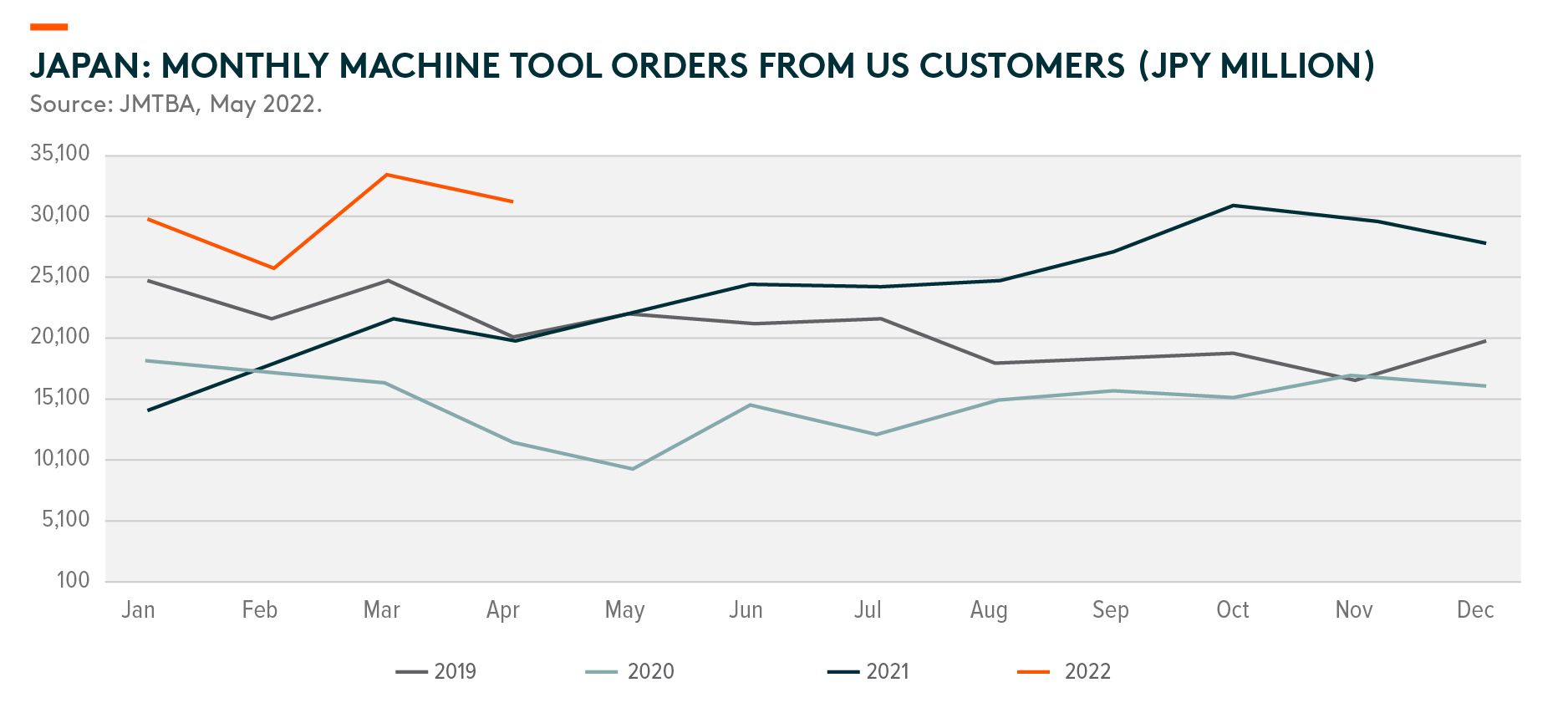
The lockdown heavily disrupted demand for Chinese automation and robotics in April and May, with significant interruptions to logistics and production during that period. In particular, the capital expenditure of small enterprises saw the greatest hit as many suffered from weak cash flows and profitability, which limited their spending interest and spending power. For larger corporate customers, their spending was mostly delayed but not canceled. Automation solution delivery and revenue recognition were mainly delayed due to logistics disruptions and labor shortages. On the contrary, according to the purchasing managers’ index (PMI) and JMTBA1 data, overall automation demand was fairly resilient and healthy in Europe and the US.
Across end market verticals, we see a divergence in the performance of demand growth. There was generally strong new order and growth momentum in end verticals that benefited from decarbonization. Meanwhile, industries with a higher mix of small enterprises have generally underperformed. Airtac’s May data suggest healthy industry growth (+10%) with demand from the battery (+110% YoY), automobile (+110% YoY), energy, and lighting (+110% YoY), and electronics (+25% YoY) markets outperforming relatively.
Supply Chain Tightness Remains the Key Challenge; Benefiting Chinese Players During Lockdown
Due to unpredictable production and logistics, China’s lockdown worsened the supply chain tightness globally given that China is one of the key production hubs. Hence, many global robotics suppliers’ lead time increases further. The supply chain tightness became the main bottleneck for automation companies to cater to customer demand. Fanuc and Yaskawa Robotics’ lead time got extended further, according to distributor channel checks, and in some cases, they were unable to provide a fixed delivery time.
For automation and robotics brands, chip availability remains a bottleneck with little signs of improvement in the near term. Recent distributor and corporate calls still cited the chip shortages as a key reason for robotics production delay. This is worse for foreign brands with more stringent supply chain management policies. Their customers are also more stringent and could take a longer time to accept new component suppliers. As a result, the industry inventory level is lower than normal.
This tightness benefits select Chinese automation and robotics suppliers due to their much shorter product lead times and more agile supply chain management. Moreover, these Chinese players only have one target market, leading to much better distributor and customer management priority. Unless we see a more certain full-scale reopening, those import substitution benefits are likely to stay for some time.
Anticipating Improving China Growth but Concerned about ex-China Growth in H2 2022
As we head into H2 2022, the base effect will lead to headline figures showing a divergence between China and ex-China growth. Last year, May was the peak for China’s automation delivery. Thus, H2 2022 will have an easier comparison. On the contrary, ex-China growth will face a high base effect in H2 2022, leading to a moderating YoY growth rate. JMTBA data might turn negative in October this year. Concerns on rate hike impacts on the developed market economy might slow the corporates’ pace of capital spending.
For the upcoming quarters, we should also anticipate some restocking activities in China. The inventory of automation solutions and components was depleted during the lockdown. As manufacturing activity recovers and demand normalizes, we expect the supply chain to gradually restock as a buffer to weather potential disruptions in the future. As such, this could drive a stronger-than-normal demand recovery.
In terms of key end applications, we believe robotics demand will stay resilient in H2 2022, benefitting from global automation needs to resolve labor availability issues. Laser application demand could take a longer time to recover following the pandemic. Part of laser demand is for general purposes, with high exposure to small enterprises. These small enterprises will only spend CAPEX when they see improving order trends and profitability. For laboratory testing demand, lower corporate profitability and tighter government budgets could slow demand in H2 2022.
Components demand is a relative bright spot. As the order lead time of automation companies remains quite long, they are still digesting the strong order and demand from prior to the pandemic lockdown. As such, the demand for components is still fairly resilient. According to Hiwin, their linear guide/ball screw production lead time remains stable (~3-3.5 months / 4 months now, vs 2-3 months / 5.5 months at the end of 2021).2