Investment Opportunities for China’s Reopening
Listen
China’s reopening has been earlier and more accelerated than the market anticipated. The U-turn on the zero-COVID policy, along with other meaningful policy shifts such as the property rescue measures and regulatory easing for big tech, now presents ideal opportunities to position for China’s economic recovery. In this article, we highlight three sectors that are major beneficiaries of China’s reopening and explain the likely drivers of their earnings growth in 2023.
China Consumer Brand
Why Was the Industry Under Pressure During COVID-19?
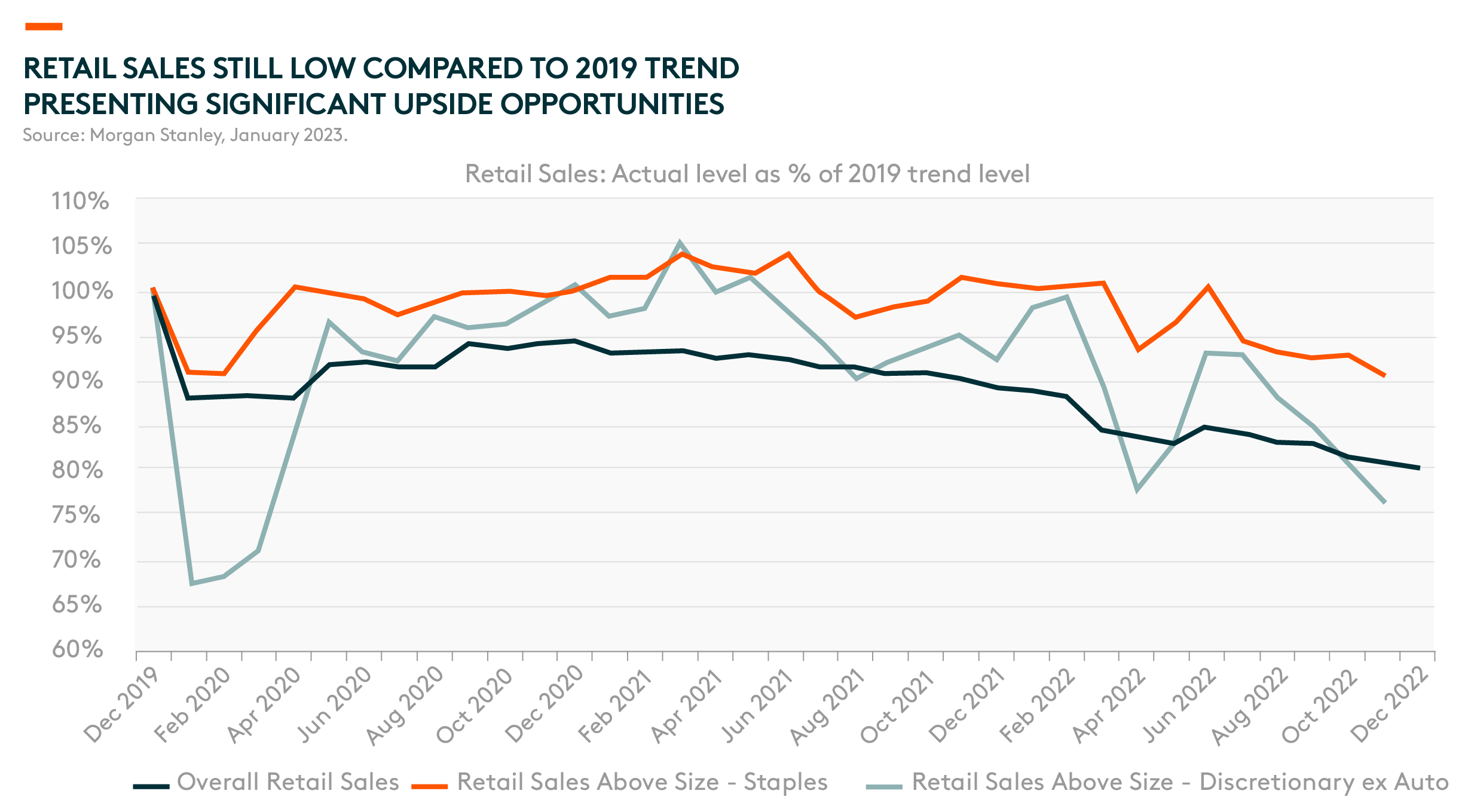
China’s consumption was heavily hit by the zero-COVID policy in 2022. Consumers couldn’t spend during lockdowns, while sentiment declined to a record low level amid tight restrictions. Overall retail sales in December 2022 remained 20% below 2019 levels, with offline activities or discretionary spending generally seeing a bigger impact.1 Thus, we expect a strong rebound in 2023, along with the country’s reopening.
Restaurants are one of the industries that were severely impacted by the pandemic. Leading companies suffered, while many smaller restaurants are expected to have gone entirely out of business. Thus, we expect larger restaurants to show a strong rebound once consumers start eating out again after reopening.
What Will the Industry’s Growth Look Like After COVID-19?
For 2023, we expect a strong earnings rebound and consumption recovery in China, with private consumption to be a key driver of economic growth. Reopening is an essential catalyst for this, along with the government’s focus on economic growth this year. According to BofA estimates, Hong Kong and US-listed key consumer names are expected to show an average 33% earnings growth in 2023, while A-share consumer names are expected to deliver 23% earnings growth.2 We feel there may be even more upside to these earnings estimates, considering China’s reopening pace has been faster than the market anticipated.
Long-Term Investment Thesis of the Theme
Population size is a key factor in consumption volume growth. Given China’s population, Chinese consumers have emerged as one of the largest consumer groups across many categories, yet penetration levels still remain low. More importantly, every year, Chinese households are increasing their affordability for consumption. This is also supported by the government’s push for common prosperity, which targets to grow the middle class in China from 400 million people in 2020 to 800 million in 2030.3
Chinese consumer brands also benefit from the strong ‘Guochao’ trend, representing the shift in preference for local brands, especially by young Chinese consumers with a strong sense of nationalism. Additionally, local brands have become much more competitive in catering to fast-changing consumer needs in China. Therefore, we believe investing in leading consumer brands is one of the best ways to ride on consumption growth in China.
China Biotech
Why Was the Industry Under Pressure During COVID-19?
China’s biotech industry was undermined during the COVID pandemic due to several reasons:
- COVID-related lockdowns impacted R&D activities, including clinical trials, due to delays in patient recruitment.
- Hospital visits by patients were restricted due to COVID-19 measures, leading to a halt in new prescription growth.
- A few companies focused more on COVID-19 drugs and vaccine-related projects and deprioritized their core pipeline growth.
What Will the Industry’s Growth Look Like After COVID-19?
The earnings growth outlook for China’s healthcare industry varies by sub-sectors. For the CRO (Contract Research Organizations) / CDMO (Contract Development and Manufacturing Companies) sub-sector, excluding COVID-related projects, we expect the growth rates to range between 20-30% for most companies.4 For example, the management incentive plan for Tigermed Consulting assumes a 21% growth for 2023.5
For large companies, we expect core business volume growth to bounce back to 10-15%, which will be further aided by their innovative drug portfolios, which will likely be above this growth rate.6 Finally, for biotech companies, many are still in the early days of profitability.
Long-Term Investment Thesis of the Theme
In China, oncology and auto-immune diseases continue to be under-treated, while the country also has significant unmet medical needs. Hence, we believe innovative biologics treatment medicine will drive growth in China’s pharmaceutical industry. Furthermore, as China’s society continues to age, the incidence of oncology and lifestyle-driven ailments will increase. We believe innovative drugs will demand premium pricing and drive favourable competitive dynamics, which gives visibility for revenues and earnings.
As industry growth rebounds in 2023, we expect sector research and development (R&D) activities will also bounce back as companies look to further deepen their research pipeline. This should benefit CRO and CDMO. Additionally, underlying biomanufacturing demand continues to be strong. Adjusting for loss of exclusivity (LOEs), global biologics sales grew at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of ~14% 2020-23e and are expected to grow at 12% CAGR from 2020-2028e.7
China Cloud Computing
Why Was the Industry Under Pressure During COVID-19?
As China relaxed COVID control measures and ceased mass testing, infection reached a peak around mid-December. According to many Chinese software companies, massive COVID infection of their clients and their own employees resulted in low attendance rates, which negatively impacted business operations. Project implementation and cash collection were delayed, while client IT spending was also reduced. As a result, Q4 2022 revenue growth of China’s software industry has been revised down at substantial scales, weighing heavily on annual growth due to higher seasonality of revenue contribution.
What Will the Industry’s Growth Look Like After COVID-19?
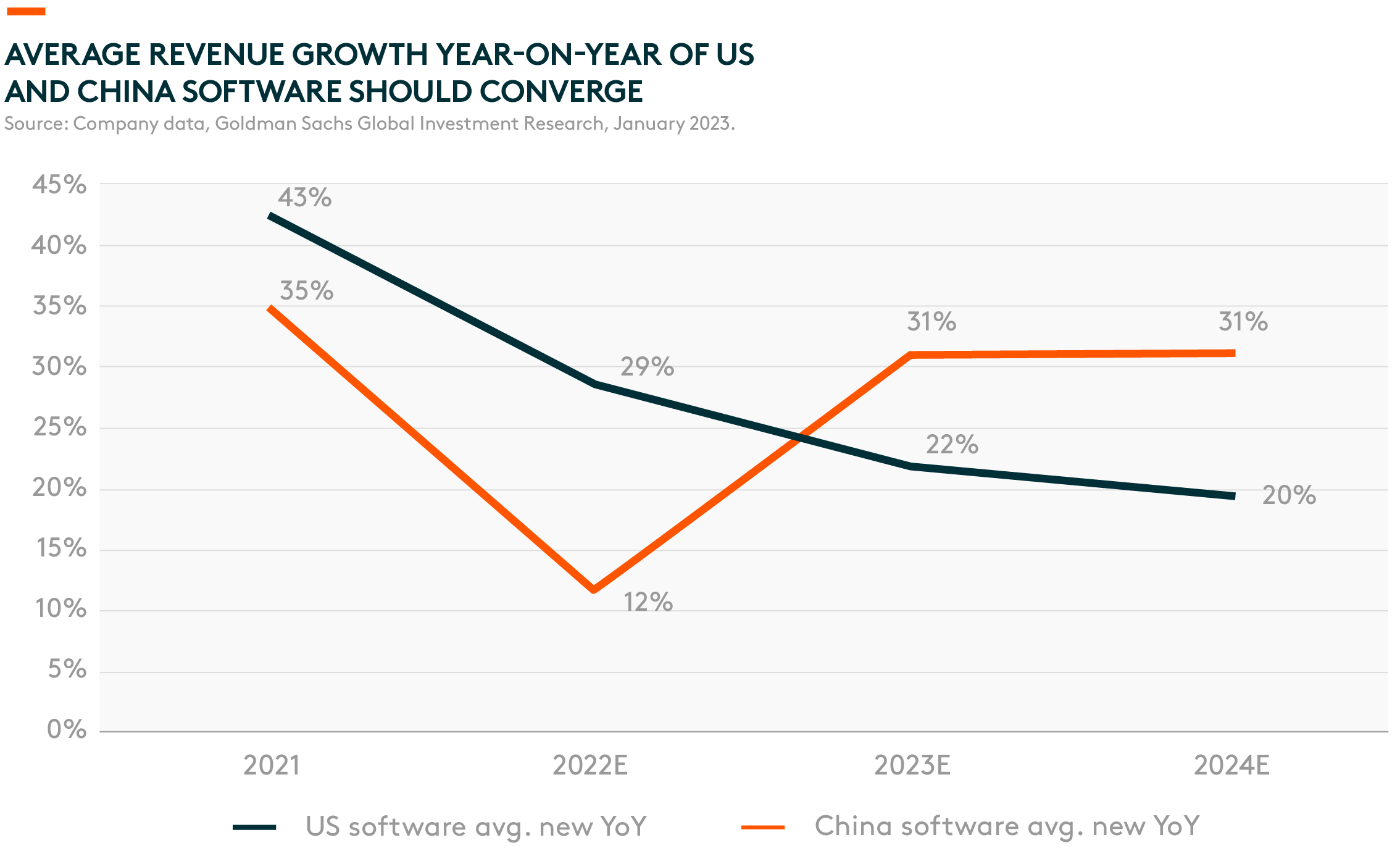
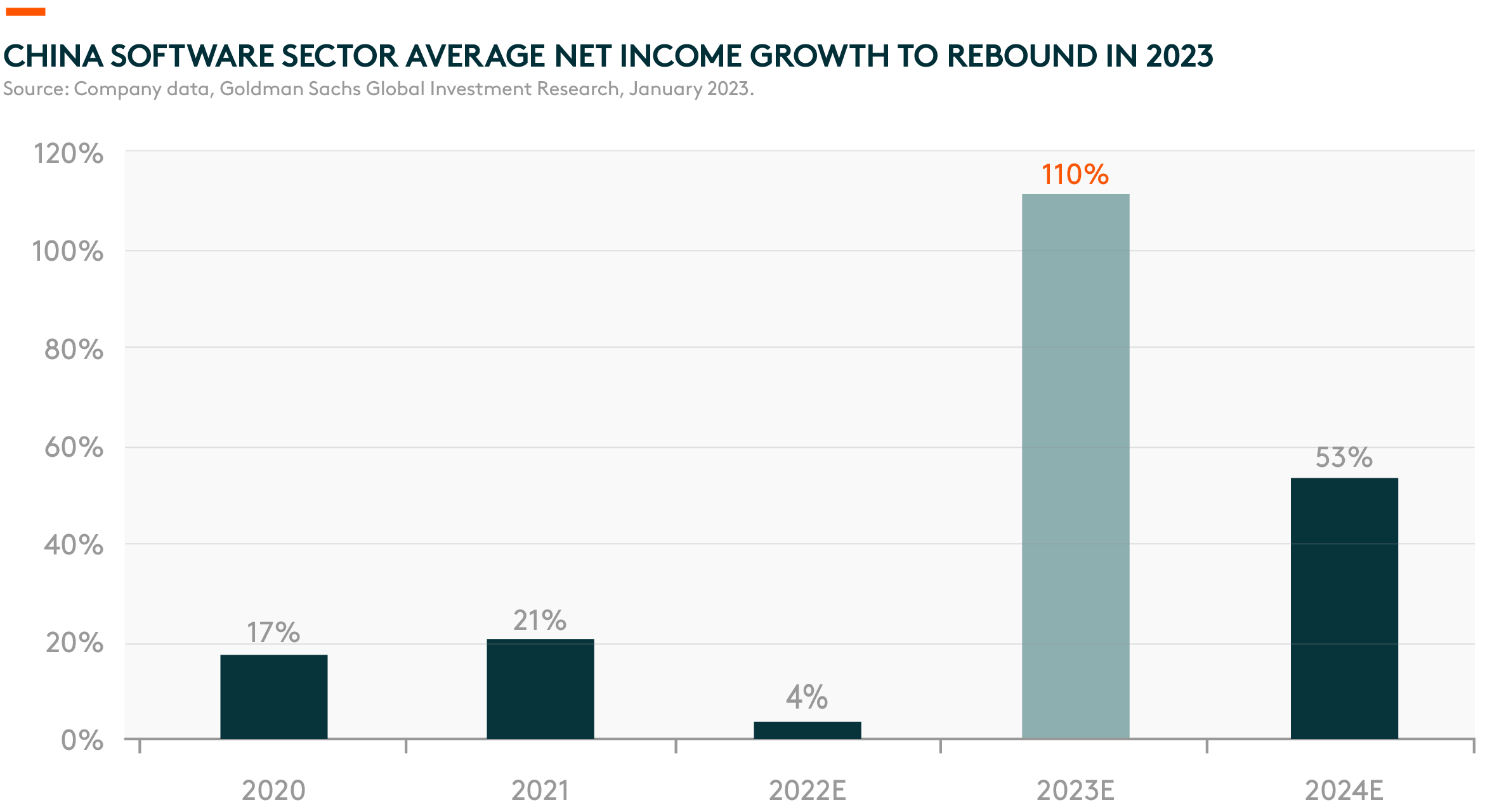
According to Goldman Sachs, the average revenue growth for China’s software sector should rebound significantly into 2023 at an estimated 31% year-on-year (y/y), compared to 12% y/y in 2022.8 Net profit growth should also accelerate to 110%, driven by better economies of scale and continuous cost control.9
China’s internet sector is expected to deliver an average 14% y/y top line growth in 2023, compared to -5% in 2022.10 According to FactSet consensus, earnings growth is expected to accelerate to 64% y/y for 2023, compared to 3% y/y for 2022.11
Long-Term Investment Thesis of the Theme
Compared to the US, where IT spending is 1% of GDP, China’s IT spending is still low at just 0.1%, of GDP, leaving significant potential to catch up.12 The digital transformation of government, military, and enterprises was severely hampered in 2022 due to macro weakness and COVID lockdowns. We expect the growth rate of IT spending to reaccelerate from 2023 onwards as China relaxes COVID control measures and the macroeconomic landscape improves.
Growing digitalization means more business operations will move onto the cloud, triggering a continuous demand for cloud computing. By verticals, China’s software industry is expected to deliver solid growth on the continuous artificial intelligence (AI) and digitalization trend and positive government support like software localization.