China Biotech: Q3 2022 Review
Listen
China’s biotech industry has undergone a downward trajectory over the last 18 months, with external news over Q3 2022 adding to the general risk-off sentiment. Chinese biotech stocks dipped on news of the US Government’s Executive Order (EO) to bolster their domestic biotech and biomanufacturing industry. However, we believe the EO’s investment is relatively small and should not negatively impact China. Elsewhere, China continues its volume-based procurement (VBP) program to increase the accessibility of drugs for patients. Overall, we maintain an optimistic outlook for services outsourcing and biotech companies, where mid to longer-term fundamentals remain intact despite near-term price movements.
Key Takeaways
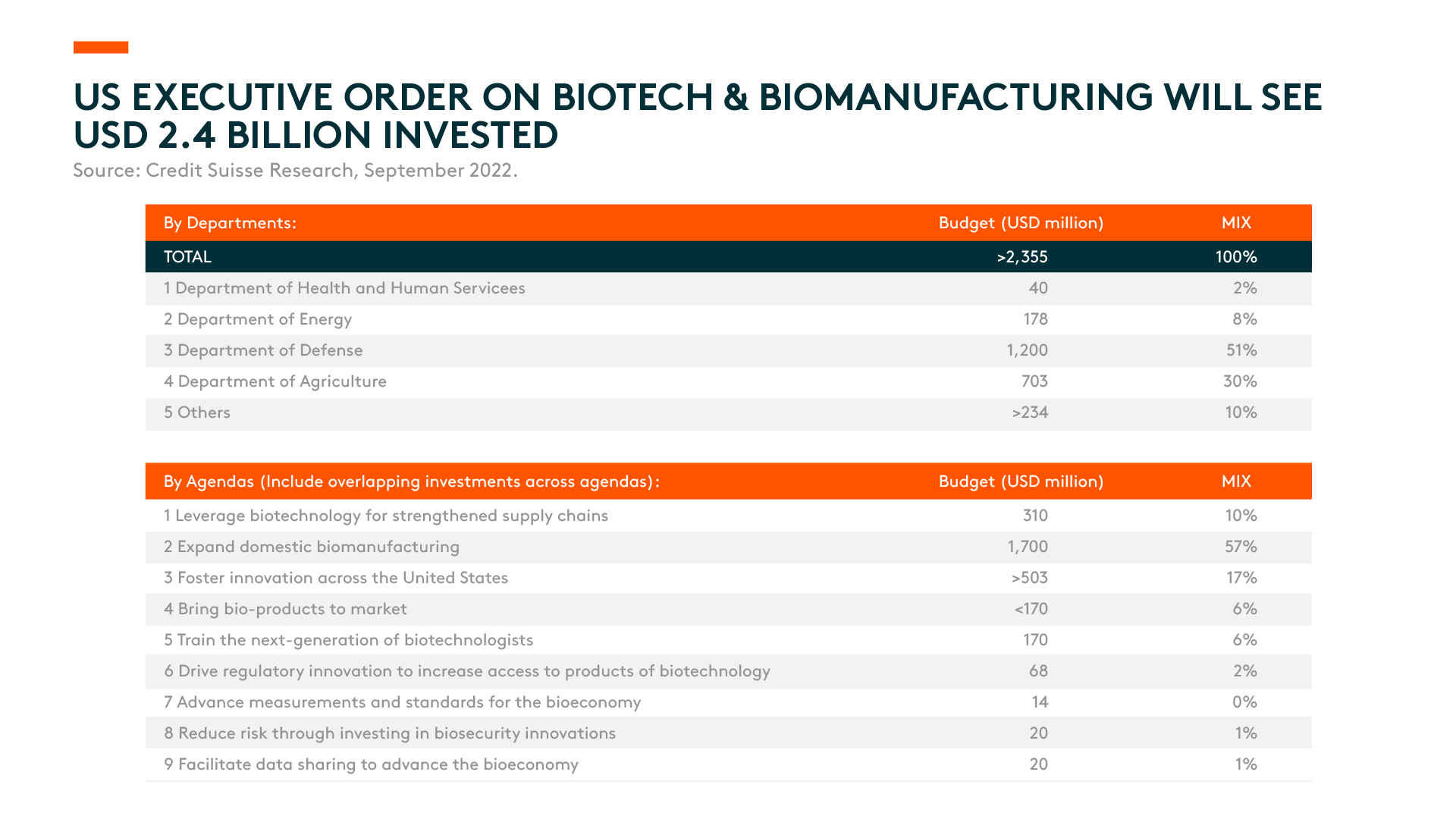
- The US Executive Order on Biotech and Biomanufacturing will see US$2.4 billion invested in expanding domestic biomanufacturing, fostering innovation in the US, and leveraging biotech to strengthen supply chains, among other initiatives.1 Although the funding plan is broad, we believe there is limited impact on China’s biomanufacturing industry as there are no specific restrictions on China or any particular restrictions on biological products, biotechnologies, supply chains, or critical raw materials.
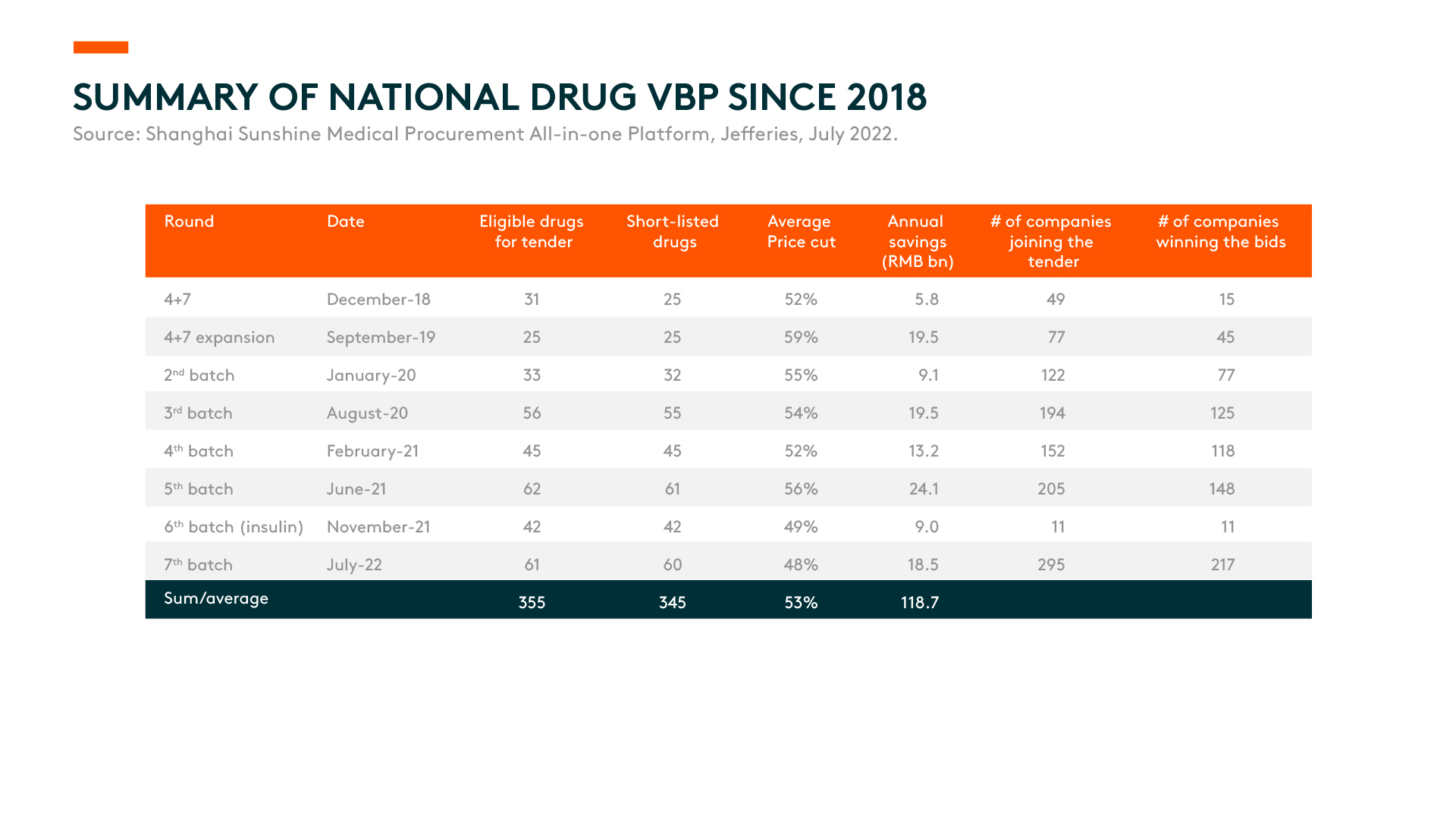
- The 7th batch of volume-based procurement (VBP) concluded with 60 drugs listed at an average price cut of 48%.2 As VBP price cuts become the new normal, we prefer companies where no single product has a high risk of price cuts or a significantly high revenue contribution.
- Overall, we believe the outlook remains positive for services outsourcing companies as demand continues to be strong. For biotech companies, we’ve seen early signs of companies re-prioritizing and have been agile in the evolving competitive landscape for their assets.
US Biotech Executive Order Has Limited Impact on Chinese Companies
On 12 September, the US Government passed an Executive Order (EO) with the aim of
- growing its domestic biomanufacturing capacity and securing supply chains,
- encouraging research and development (R&D) to drive medical breakthroughs, and
- building and protecting the US biotechnology ecosystem, including data collection, data security, data sharing with partners, skilled workforce, etc.
The US White House hosted a biotech summit days later, releasing more details on the specific funding budget. Around US$2.4 billion will be allocated through the EO to advance biotech/biomanufacturing initiatives to lower prices, create jobs, and strengthen supply chains.3 In addition, the White House laid out specific agendas to be carried out by the Department of Health and Human Services (DHHS), Department of Energy (DoE), Department of Defense (DoD), and US Department of Agriculture (USDA), among others. The DoD and USDA will account for over 80% of the total budget.4
The largest agenda item is the expansion of domestic biomanufacturing, with a total of US$1.7 billion to be funded by the DoD (US$1.2 billion) and USDA (US$0.5 billion).5 The DoD will invest US$1 billion in bio-industrial domestic manufacturing infrastructure over five years and an additional US$200 million to support biosecurity and cybersecurity posture enhancements for commercial and defence supply chains.6 The DoD expects emerging biomanufacturing capabilities will help the department address logistical challenges, while biotechnology will enable it to source mission-critical materials domestically without relying on fragile supply chains.
The USDA plans to utilize over US $700 million in funding to provide tools, resources, and scientific research to ensure American farmers and producers remain globally competitive. Of that amount, US$500 million will be made available to the domestic biomanufacturing expansion agenda item to support independent, innovative, and sustainable American fertilizer production in supplying American farmers.7
The funding plan outlined by the US government will strengthen the US’ competitiveness in bio-alternatives such as bio-based chemicals and plastics for industrial processes. However, the EO is nowhere near as powerful when compared to the US$52 billion investment in the ‘CHIPS and Science Act’. Besides, the EO has limited impact on China’s biomanufacturing industry at this stage since it doesn’t have any specific restrictions on China, nor does it mention any specific restrictions on biological products, biotechnologies, supply chains, or key raw materials.
Latest Round of Volume Based Procurement Sees 48% Average Price Cut to 60 Drugs
In the 7th batch of volume-based procurement (VBP), 327 bids from 217 manufacturers made the list with an average selling price (ASP) cut of 48%.8 This is compared to -49% in the 6th batch (which consists largely of insulin) and an average price cut of 54% over the previous six rounds of VBP.9 Similar to previous batches, domestic players continued to dominate the 7th round, given they were the most flexible on pricing, and trading margins with serious volume gain.
The 7th batch VBP marks the scale of RMB 87 billion in terms of 2021 public hospital sales. Based on contracted procurement volume, we estimate that RMB 18.5 billion will be saved each year from this round of VBP.10 The VBP prices will take effect from November 2022.
We note that the 320 drugs listed in the seven VBP batches combined cover around 35% of the chemical drugs and biologics sales from public hospitals.
Overall Outlook Remains Positive
With a high base in 2022 for CRO (contract research organization) and CMO (contract manufacturing organization) companies from COVID revenues, the market is likely to get more optimistic until there is more visibility of 2023 revenue delivery, in our view. Most companies see limited impact from inflation, which they can pass down to downstream clients, and the backlog visibility remains very high. Moreover, capacity expansion remains in progress, driven by robust client demand.
For biotech companies, we believe re-prioritizing pipelines to optimize resource allocation and commercialization becomes the next area of focus. We have seen early signs of companies re-prioritizing and have been agile in the evolving competitive landscape for their assets. For more established companies, the sales recovery post-COVID lockdowns will be the focus post-opening up.