What is Specialized and Sophisticated “Little Giant” Enterprises?
Global X China Little Giant ETF (2815)
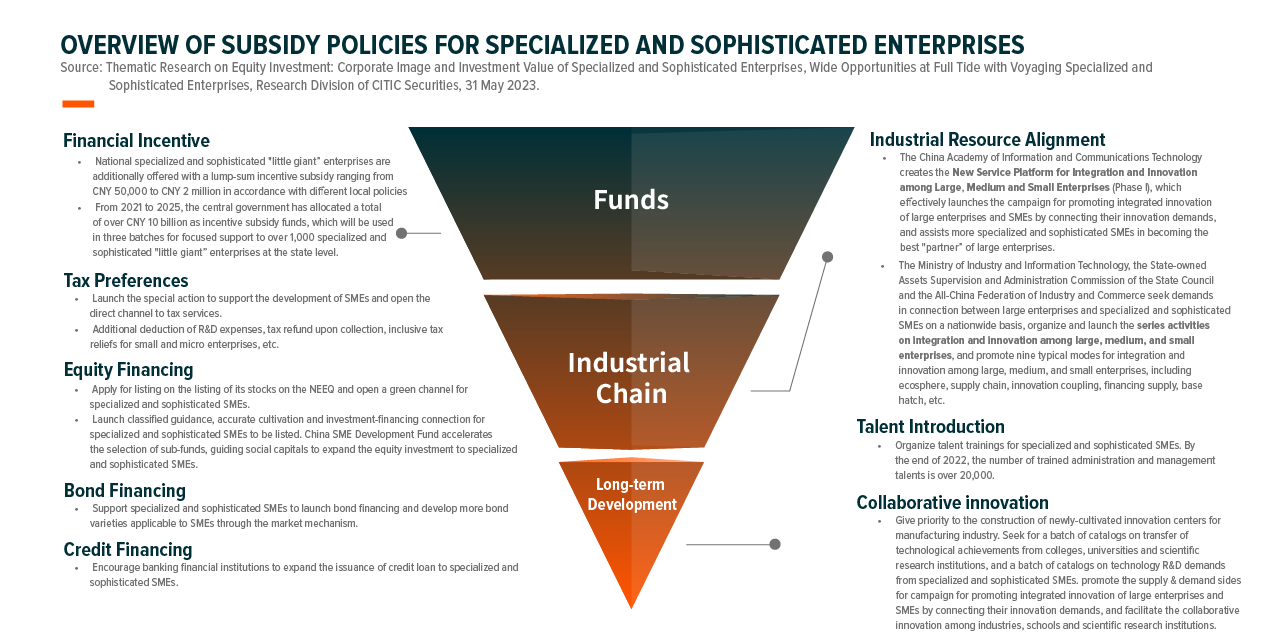
Broad support
Selection as a ‘Little Giant’ company entails broad support from various governments and organizations
High growth potential
Constituents possess strong innovative capabilities and generally have higher ROE than market average
Differentiated small and mid-cap fund
Products invested in small to mid-cap A-share stock with high growth potential are relatively scarce

Why Choosing the Specialized and Sophisticated "Little Giant" Enterprises?
As the stage of China's economy transforms from rapid growth to high-quality development, and the economic growth slows down, the weakening advantage of traditional industries has caused great changes to the supply-demand structure. In recent years, deglobalization, Sino-US trade friction and sluggishness in global economy have also incurred risks and challenges. The proportion of manufacturing industry in foreign direct investments has decreased from 70.95% in 2004 to 19.44% in 2021, and China's degree of dependence on foreign trade has also decreased from 62.63% in 2006 to 33.71% in 20211. Accelerating independent innovation in science and technology and developing specialized and sophisticated enterprises is the key to realizing the transformation of China's economic structure and making China play an initiative role in international circulation. This makes the economic development shift gear from being driven by traditional production factors or investment to being driven by innovation, keep improving the quality and level of supply and promote the high-quality development with sustaining innovation of technologies and products.
“Specialized and sophisticated SMEs” refer to those SMEs that excel in professionalism, refinement, uniqueness, and possess outstanding innovation capabilities. Among them, the "Little Giant" enterprises that have emerged through sustained and rapid development are the leading SMEs in the realm of specialized, high-end, and innovation-driven SMEs. These "Little Giant" enterprises focus on niche markets, exhibit strong innovative capabilities, and demonstrate good growth potential. They possess core technologies and products in strategic areas such as semiconductors, pharmaceuticals, clean energy, advanced manufacturing, and play a significant role in driving the pace of "supply-side reforms". Therefore, the importance and influence of “Specialized and sophisticated Little Giant” enterprises within the high-quality development system are increasing day by day.
Research and Analysis
Transformation & development of China's economic structure
For 40 years, China's manufacturing sector has been growing rapidly. In 2010, China had its output value of manufacturing sector exceed that of the U.S. And became the world's largest manufacturing country. However, after China has entered a new normal in economic development, it is further shown that there are voids for core technologies in the industrial chain, and that the high-tech field is not strong enough, especially the feature that our manufacturing industry is big but not strong.
Since the implementation of "making China strong in manufacturing", China's manufacturing sector have been advancing from "three lows and one weak" (low added value, low technology, low quality and weak brands) to "three highs and one strong" (high added value, high technology, high quality and strong brands), progressing from lower-end manufacturing to top technology and high-end manufacturing & services. Specialized and sophisticated SMEs as an important participant in technological innovation, including specialized and sophisticated "Little Giant" enterprises as an outstanding representative for the transformation China's economic structure, have great potential of growth and bring significant investment opportunities for investors.

Government’s Support
The Chinese policies provide active support to the development of specialized and sophisticated "Little Giant" enterprises and, starting with 6 orientations including fund support, collaborative innovation, talent support, brand market, enterprise transformation and accurate connection services, offer them a series of favors together and jointly build the service ecology for specialized and sophisticated "Little Giant" enterprises with multiple players under the domination by the government.
The growth of "Little Giant" enterprises is also significant to the industrial transformation for local governments. First, from the most obvious perspective, the "Little Giant" enterprises are leaders of technological innovation that are advanced in technological R&D, product innovation and solutions. Their development makes cutting-edge technological achievements, as well as technological progress and application that may improve local science & technology and innovation. Secondly, the "Little Giant" enterprises are usually engaged in emerging or high-added-value industries, and their development enables to push forward the adjustment and optimization to industrial structure. By guiding the development of new technologies, new modes, and new business formats, they can promote local industries to be more competitive and sustainable and make urban industries livelier and more diversified. Finally, the implementation and rapid development of "Little Giant" enterprises can attract enterprises at other links of the industrial chain and form a regional industry cluster. The collection of talents and technologies incurred by this regional industry cluster facilitates the accelerating transformation of local industries and creates unique industrial advantage for cities so as to make them more influential and attractive in global competition.
Insight to Global X China Little Giant ETF: FAQ
How is the long-term prospect of Global X China Little Giant ETF?
As China’s economy is transforming to the stage of high-quality development, the requirement for enterprises has transformed from the emphasis on expanding and transformation of scale to the focus on improving the capability of innovation. As the leader of SMEs, specialized and sophisticated "Little Giant" enterprises undertakes the key mission to solve the problems of restriction to core technologies in key fields and void in the high-tech field. According to the data of Patsnap, The invention patent density of "little giants" is nearly three times higher than that of the enterprises on the NSE. In comparison, the invention patent density of the enterprises listed on the GEM is 70.6 effective invention patents per 1,000 persons, and that of the enterprises listed on the NSE is 26.4 effective invention patents per 1,000 persons, the invention patent density of "little giants" is about 1.1 times higher than that of the enterprises listed on the STAR Market2. Therefore, it is a strategic emphasis for the upcoming transformation of China’s economic structure and future industry layout to keep cultivating and supporting the development of "Little Giant" enterprises.
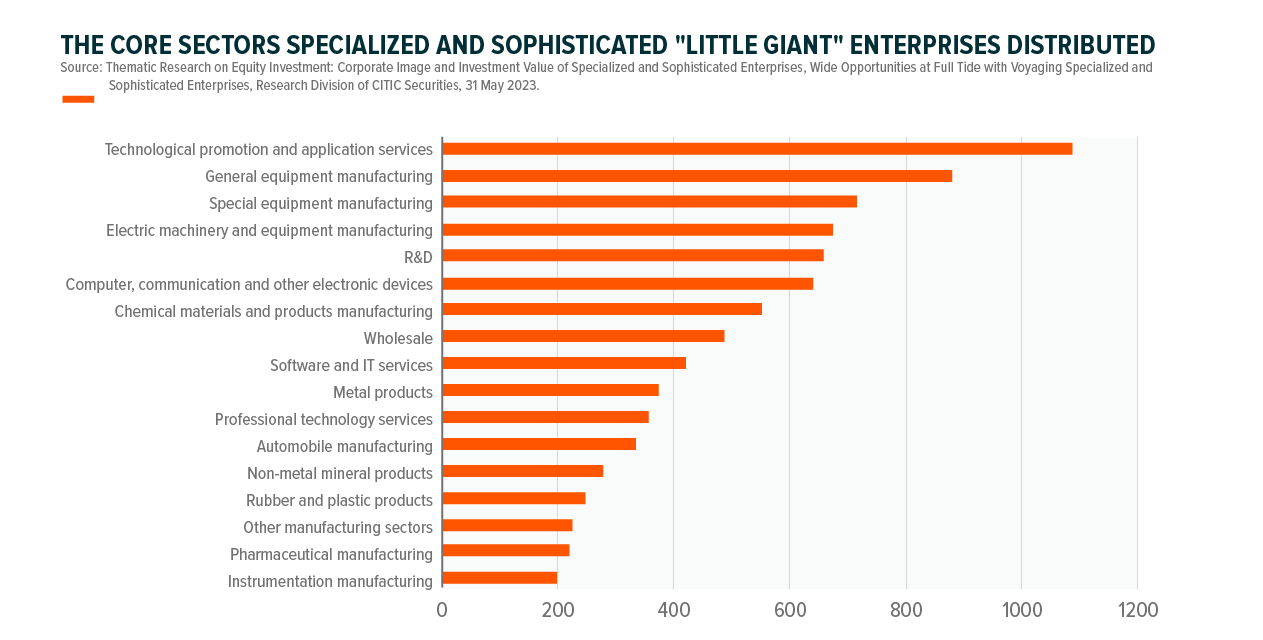
In what industries are specialized and sophisticated "Little Giant" enterprises distributed?
There are over 10,000 manufacturing enterprises of the 12,000 cultivated "Little Giant" enterprises. Over 40% of the "Little Giant" enterprises runs their business in the fields of new materials, new-generation IT, new energy and ICV (Intelligent Connected Vehicle); over 60% of them focus on industrial base. Based on the distribution of industries, most of the "Little Giant" enterprises focus on manufacturing and different high-tech industries.
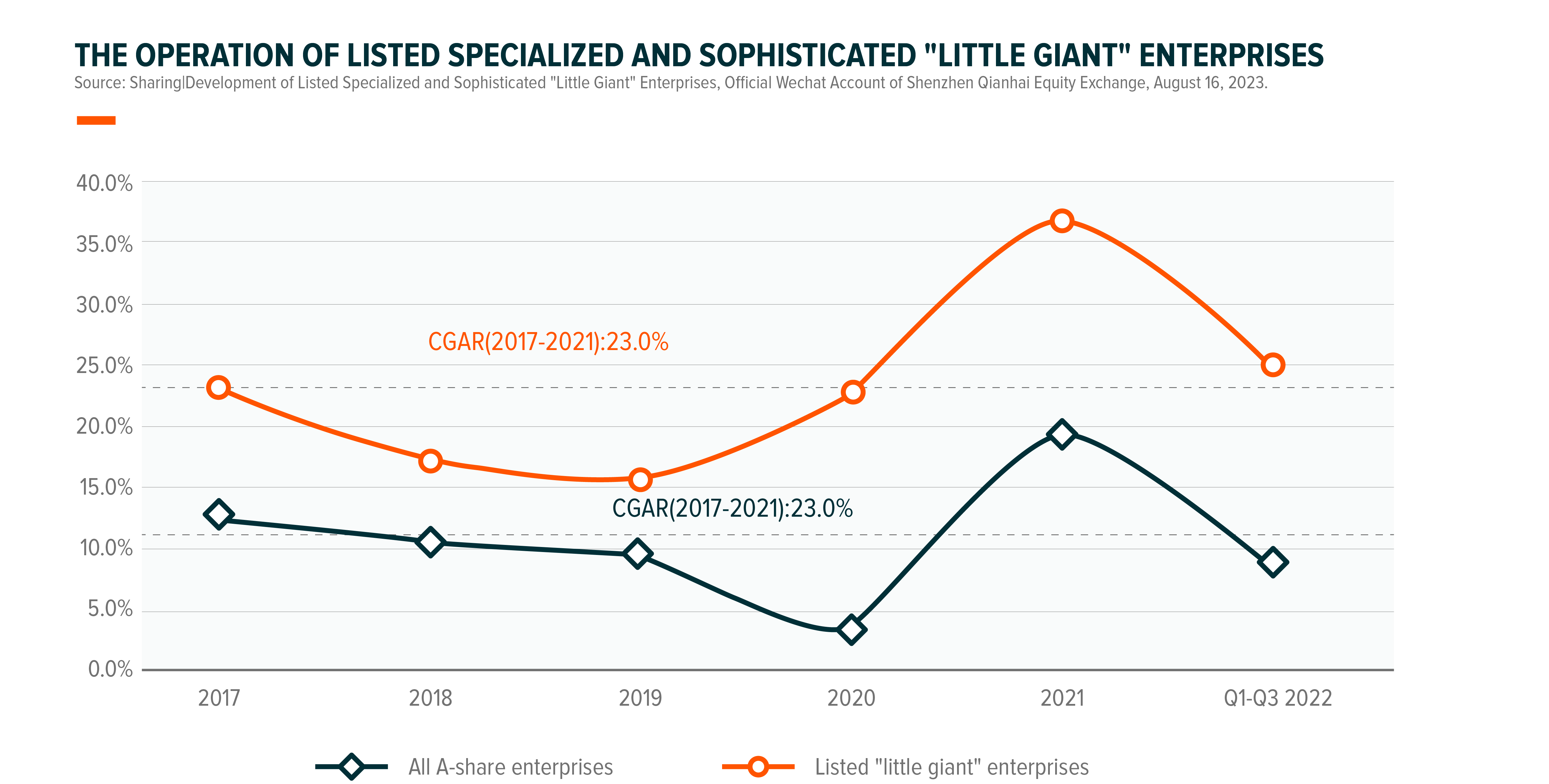
How is the operation of listed specialized and sophisticated "Little Giant" enterprises?
From 2017 to 2021, the annual compound growth rate of China’s "Little Giant" enterprises reaches 23%, which is 12.3% more than that of all the A-share enterprises. Looking further ahead, in 2020, due to the influence of COVID-19 pandemic, the revenue growth of all the A-share enterprises declined rapidly from 9.4% in 2019 to 3.9% in 2020; however, the revenue growth of listed "Little Giant" enterprises bucked the rate, expanding to 22.8%; since 2022, despite the repeated COVID-19 pandemic in China, foreign geopolitical issues and other complex factors, the average business revenue growth of "Little Giant" enterprises in the first three quarters of 2022 is still higher than that before the COVID-19 pandemic broke out, and is higher than that of all the A-share enterprises in the same period. The outstanding performance of "Little Giant" enterprises in recent years has shown their flexibility in business operation.
What is the key advantage of specialized and sophisticated "Little Giant" enterprises?
The key advantage of specialized and sophisticated "Little Giant" enterprises is their own technological power and their continuous innovation. Most of the "Little Giant" enterprises specialize in niche markets for as long as 16 years on average3, and the R&D expenses are obviously higher than those of the comparable companies.
Putting the 12,000 specialized and sophisticated "little giants" enterprises on the growth gradient of "specialized and sophisticated SMEs - specialized and sophisticated "little giants" enterprises - single champion in the manufacturing industry", the "little giants" are characterized by the following factors The technological volume (total number of patent applications), technological quality (percentage of patents for inventions), technological influence (total number of citations of patents), and technological globalization (total number of PCT patents) of the "little giants" are about 1-3 times higher than that of the specialized and sophisticated SMEs. Compared with the manufacturing industry champions, there is still a gap of nearly 10 times between the "little giants" and them in terms of various indicators. Especially in terms of PCT patents, the average number of PCT patents owned by single champion enterprises is 59, while that of "little giants" is only about 1.65, which is nearly 36 times of the growth space between the two. 4.
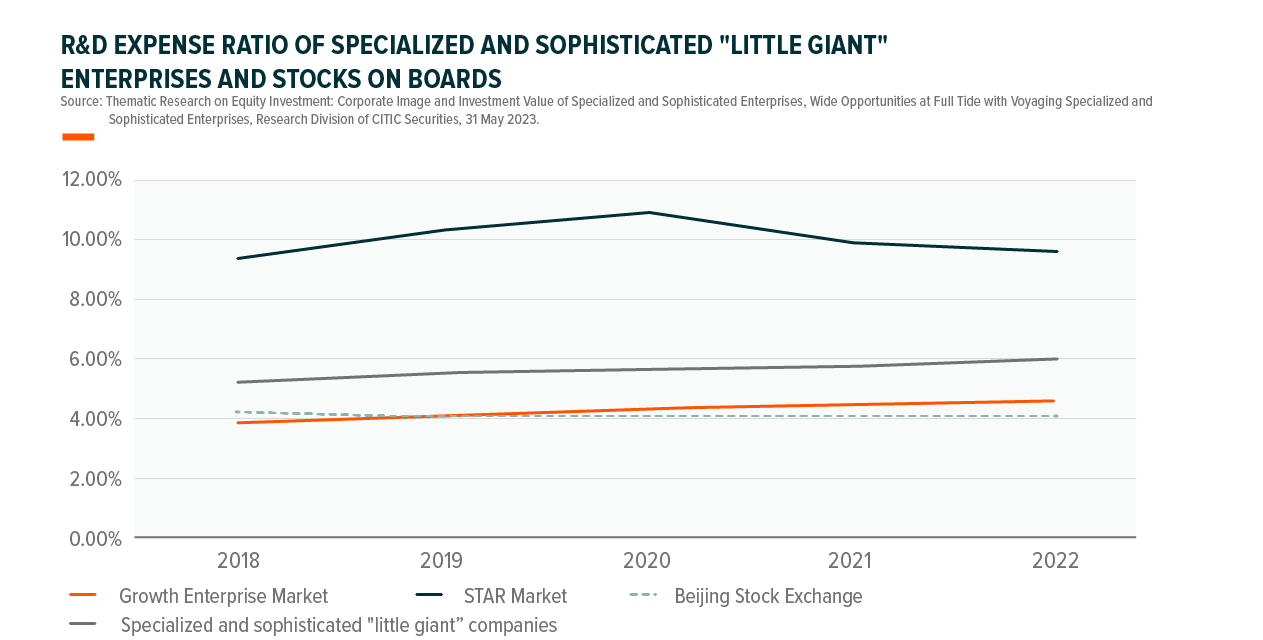
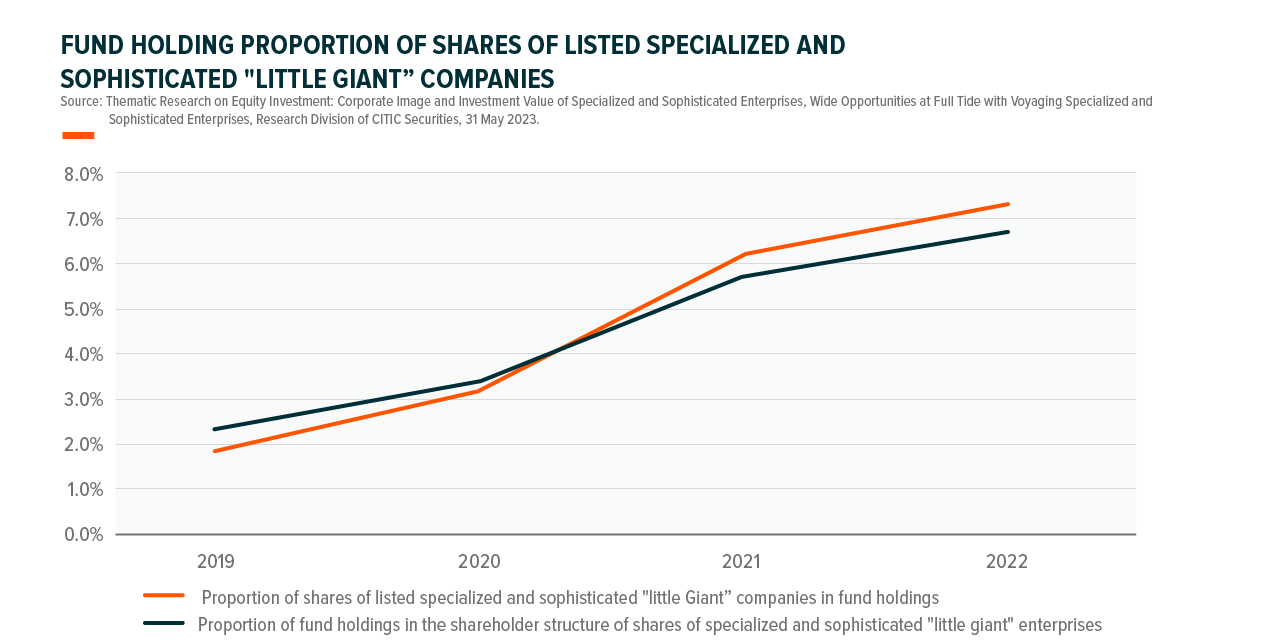
To what extent are the specialized and sophisticated "Little Giant" enterprises recognized by investment institutions?
The proportion of shares of specialized and sophisticated "Little Giant" enterprises whose position is held by China’s public offering funds has a great increase from 1.9% in 2019 to 7.4% in 2022; the ratio of fund holdings in the shareholder structure of shares of specialized and sophisticated "Little Giant" enterprises is also gradually increasing, and the shares of specialized and sophisticated "Little Giant" enterprises are also more recognized by institution investors.
How do China's "Little Giant" enterprises develop in the highly competitive market environment?
China's "Little Giant" enterprises have different "moats" from those for the high-tech enterprises of developed economies.
First, China’s large manufacturing industry has ranked first in the world for 13 years5 and has a large domestic substitution market of core technologies and products in key fields. Such a large scale offers a wide development space for China's "Little Giant" enterprises to effectively give a play to the scale effect and lower the cost.
Second, Chinese government's economic transformation plan injects great motivation to high-tech enterprises. Most of China's "Little Giant" enterprises have a strong sense of competition and constant sense of innovation. With the powerful market scale and policy supports, China's "Little Giant" enterprises are expected to rapidly improve their core technologies in the future.
Finally, China has large resource of talents as the key power to push forward technological development and social progress. In the transformation from population dividend to talent dividend, the numbers of scientists and engineers grow quickly, along with the proportion of students back from overseas, and the labor structure tends to move up. The huge "talent dividend" offers strong supports to the continuous innovation of "Little Giant" enterprises and lays a solid foundation for the transformation of China's economic structure to be driven by innovation.
Why ETF?
2815 Global X China Little Giant ETF
Global X China Little Giant ETF
| Stock Code | 2815 (HKD) # |
| Underlying Index | Solactive China Little Giant Index NTR * |
Ongoing Charges Over A Year^ | 0.68% |
| Inception Date | 20 Nov 2023 |
# Investment involves risk. Before making any investment decision to invest in the Fund, investors should read the Fund’s Prospectus for details and the risk factors. Visit Global X ETFs Hong Kong website for more details relating to this Fund (including but not limited to the Fund’s iNAV, market price, performance, daily holdings and tracking difference / error).
* The underlying index is a net total return, free-float market capitalization-weighted index that provides the net total return on investments. The net total return index is an index whose performance reflects the reinvestment of dividends or annual interest payments, net of any withholding taxes (including any special charges).
^ The Fund adopts a single management fee structure, whereby a single flat fee will be paid out of the assets of the Fund to cover all of the costs, fees and expenses of the Fund. Click [?] to learn more.
Why Global X ETFs?