Implications and Opportunities of AI
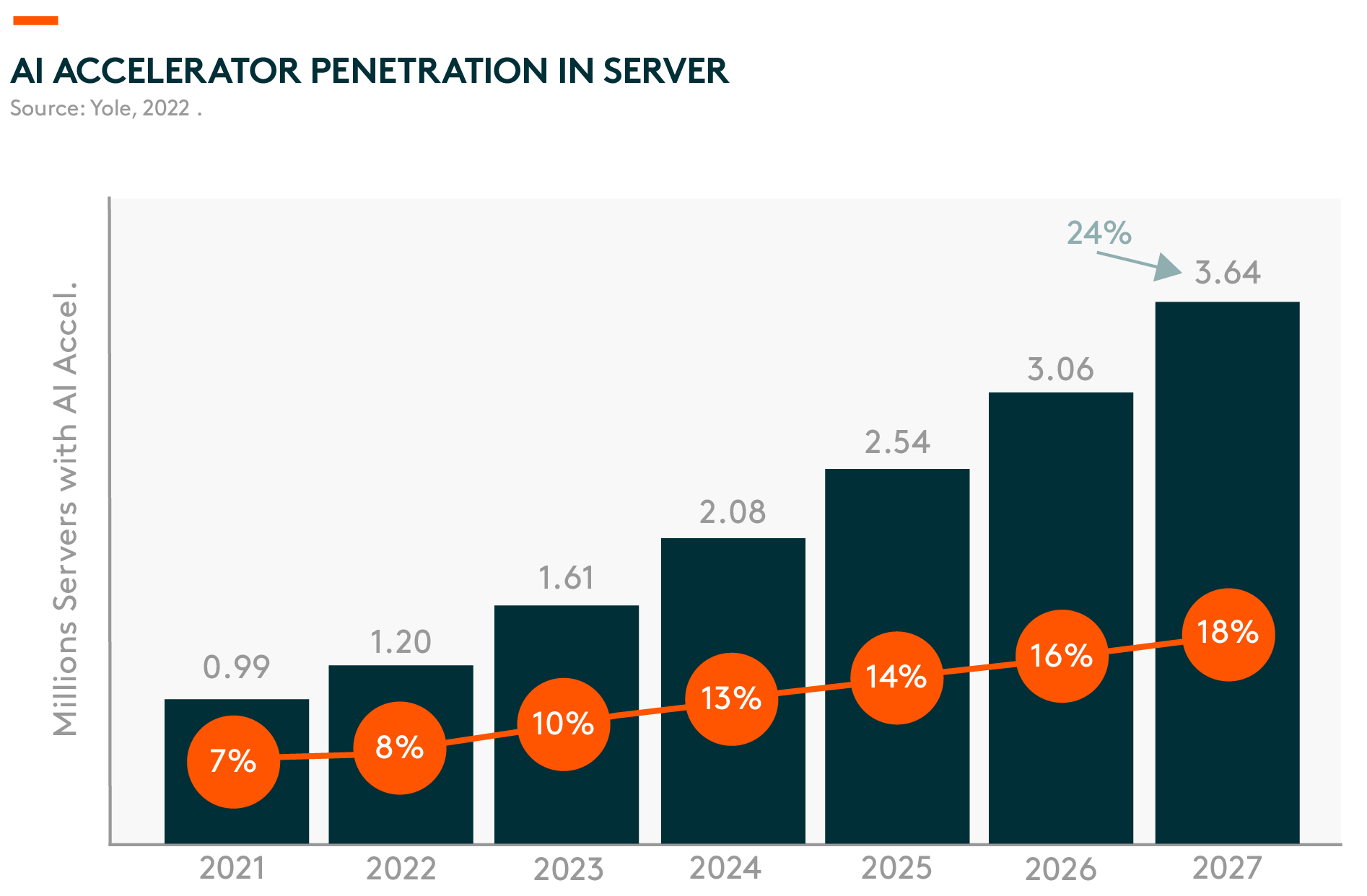
The success story of ChatGPT’s commercialization led to great expectations that artificial intelligence (AI) technology will create lucrative new business models and nurture lots of new tech companies. Meanwhile, its development will need lots of semiconductors. For reference, AI accelerator penetration is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 24% between 2021 and 2027 1. This will benefit Asia and China’s high-performance computing-related semiconductor supply chains.
Q: What is Generative AI?
Generative AI describes algorithms (such as ChatGPT) that can be used to create new content, including audio, code, images, text, videos, etc. ChatGPT is the latest natural language model launched by OpenAI and trained on Microsoft Azure’s supercomputing infrastructure. The model is trained using Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF). ChatGPT is tuned from a model in the GPT-3.5 series, which finished training in early 2022.
Q: What Potential Business Models Could Spawn from Generative AI?
1. Support other products built on an application programming interface (API): Companies which own large AI models can provide API services for other companies to build software/applications on top of its model and cloud services. Currently, services are priced per word/image. For example, a high-resolution image output of 1024×1024 pixels generated by DALL.E (Open AI’s image model) costs $0.02/image 2.
Hyperscale cloud service providers all offer different versions of AI capabilities. For example, Google Cloud and Amazon’s cloud both provide AI capabilities as API services. Differentiating factors will be in the type of tasks and capabilities of the model itself. As a result, there are ample opportunities for companies to innovate with access to large AI models via API.
It’s likely that GPT models can be leveraged by metaverse builders to help generate content and write code. More specifically, GPT can produce interactive features and representations of virtual settings within metaverse worlds and provide more immersive experiences to users if specifically trained for virtual settings.
2. Search: Google works by crawling billions of web pages, indexing that content, and then ranking it in order of the most relevant answers. It then spits out a list of links for the user to click through. ChatGPT offers a single answer based on its own search and synthesis of that information. OpenAI is working on a system called WebGPT, which it hopes will lead to a more accurate answer to search queries and also include source citations.
Q: How Advanced Are China’s AI Capabilities Compared to Developed Markets Like the US?
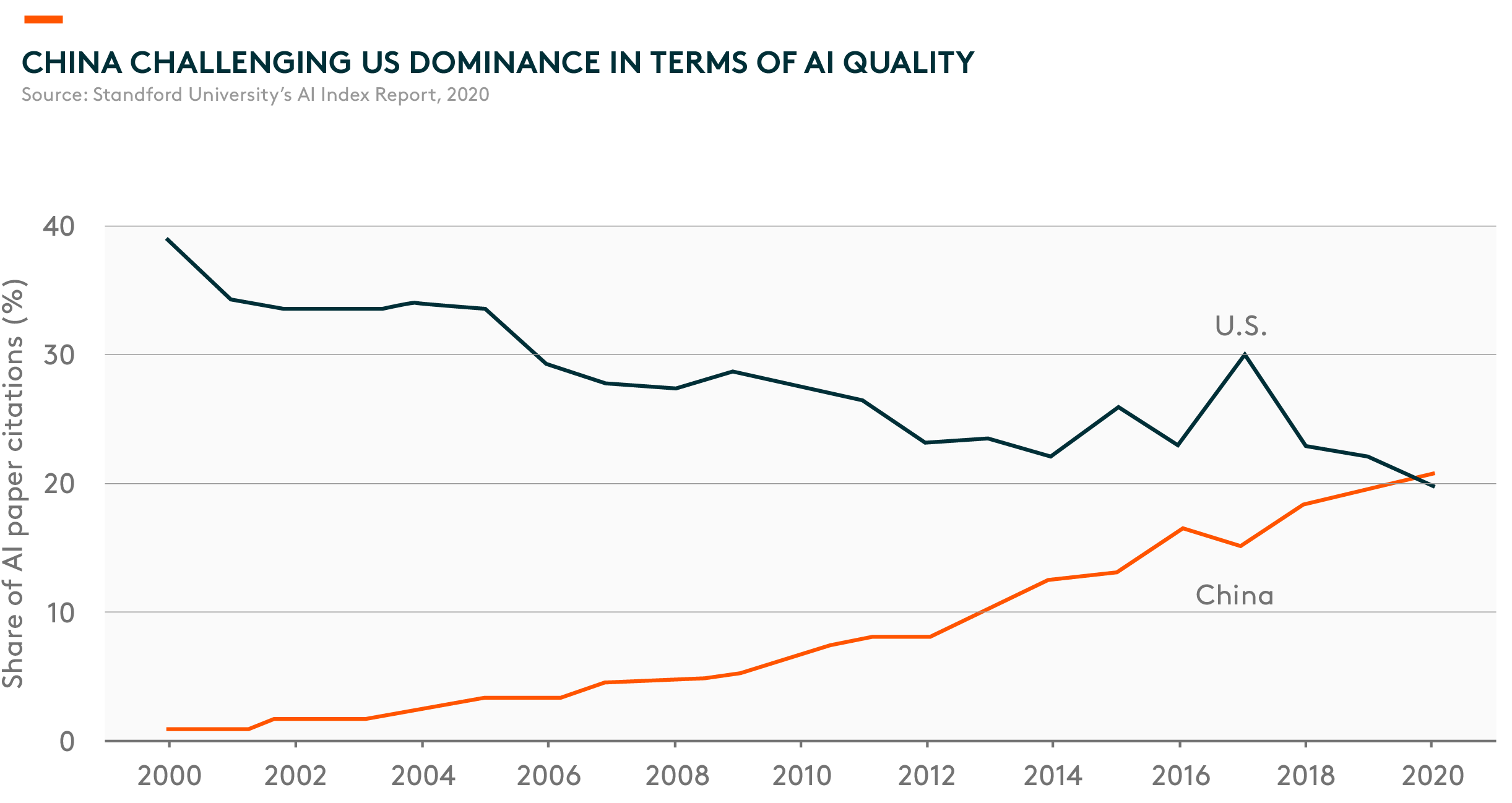
In the past decade, China has built a solid foundation to support its AI economy and made significant contributions to AI globally. China ranks number one in terms of the total number of AI-related research papers. AI research often leads to real-world applications, which we’ve seen rapid growth in China. According to Nikkei Asia, China produced 43,000 AI papers in 2021, roughly twice as many as the US, and contributed to one-third of AI journal papers worldwide 3. According to Stanford University’s AI Index Report (2020), China has also surpassed the US regarding the share of AI paper citations 4.
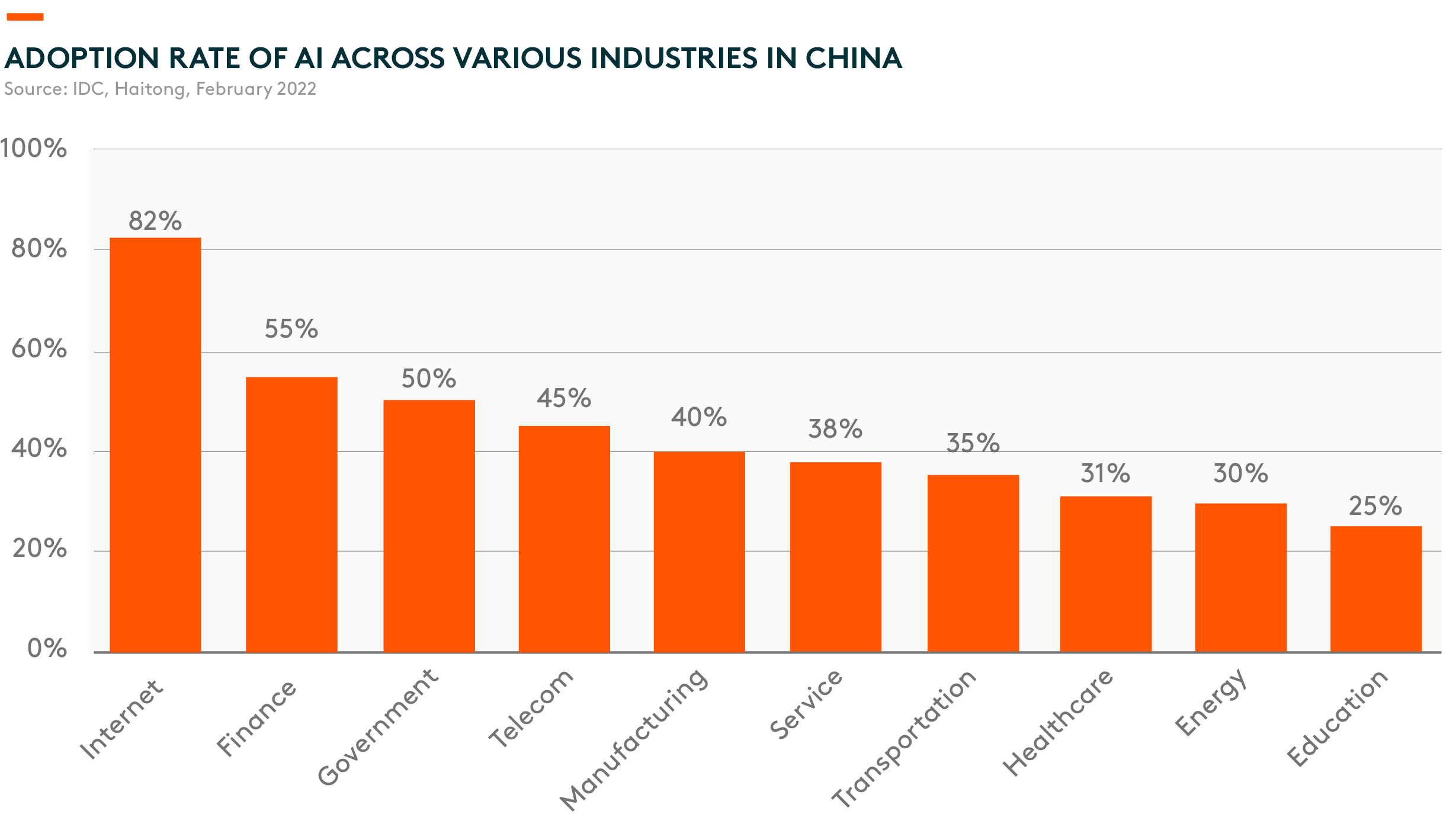
Today, AI adoption has started to prevail in many industries including finance, retail, and high-tech. The Chinese government has already released supportive policy guidelines to foster investments in AI-related fields.
Q: Are There Any Generative AI Engines Developed by Chinese Companies?
Baidu is positioned to be one of the leaders in generative AI in China. Baidu has had an early start on AI technology, particularly on natural language processing (NLP), given the close synergy to its core search business. According to the company, Baidu’s own generative AI product, ERNIE Bot, is expected to complete beta testing and be open to the public in March 2023 5. The underlying model of ERNIE 3.0 fuses an auto-regressive network and an auto-encoding network. Hence, the trained model can be easily tailored for both natural language understanding and generation tasks with zero-shot learning, few-shot learning, or fine-tuning.
Besides Baidu, companies like ByteDance, Alibaba, and Tencent also have the potential and have shown ambition to develop generative AI, given the sheer amount of data these companies have on hand. ByteDance has always utilized algorithms to analyze user preferences. Therefore, content generation using AI technology, whether for text, image, or video format, could blend in naturally with its existing businesses. Additionally, the development of generative AI could help improve the overall monetization/pricing opportunities for Baidu, Alibaba, and Tencent’s cloud services.
Given the amount of computing power required and the significant cost associated with each time a model is trained and updated, large companies with a deep bench of cash on hand, in our view, will be better positioned to tap into this field.
Q: Does China Have Any Unique Competitive Advantages in this Space?
First of all, most of the AI applications that have been widely adopted in China to date have been in consumer-facing industries like internet, propelled by the world’s largest internet user base. Internet platforms have seen phenomenal growth over the past decade, underpinning a strong investment cycle for cloud computing-related infrastructure. This has set a good foundation in terms of computing power, data, and training models required for AI development.
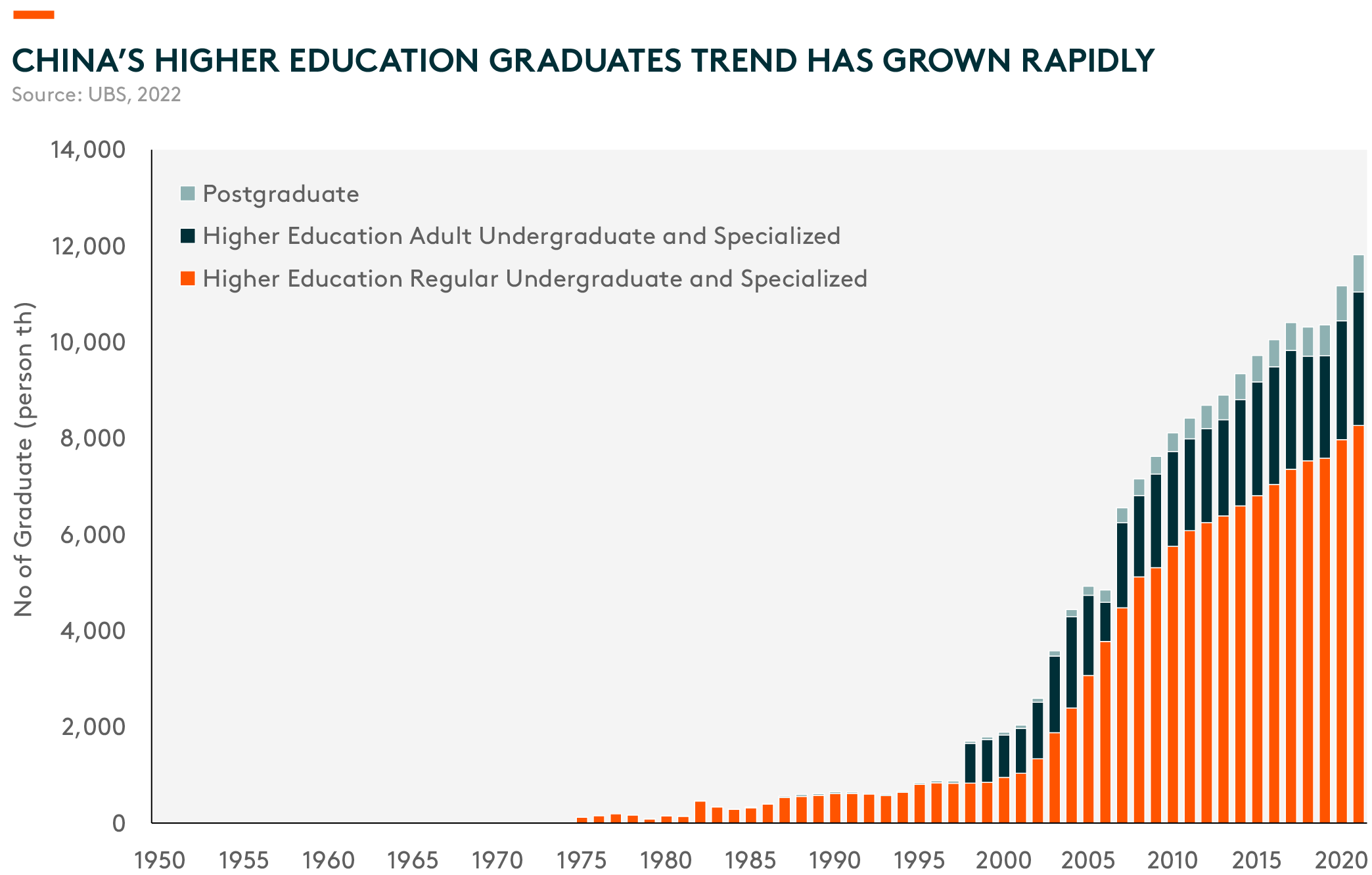
Secondly, China’s comparative advantage lies in its huge engineering talent pool. Tertiary attainment ratio among 18–22 years-old rose from 10% in 2000 to 49% in 2019. The large pool of engineers, especially software engineers, will continue to support strong growth in AI development.
Q: Which Sectors Across Asia Will Benefit the Most from Generative AI?
Asia and China’s semiconductor industries should benefit from the infrastructure investment required for generative AI. The development of advanced AI models and the ensuing blossom of new products will require significant investment in computing power to support its operations. Yole projects AI accelerator penetration to increase from 8% in 2022 to 18% in 2027, representing a CAGR of 24% from 2021 to 2027 6. This will benefit Asia and China’s high-performance computing-related semiconductor supply chains, including:
- Asia foundries. An increase in demand for AI accelerators (i.e. GPU, ASIC 7) will benefit the foundry industry, as most AI accelerators are produced by fabless, which relies on foundries to produce their chips. Asian foundries have over 90% market share globally 8.
- Design service and integrated circuit (IC) design companies. There are a number of companies in Asia that provide design services for ASIC chips in AI accelerators. MediaTek, for example, has an ASIC division focusing on high-performance computing.
- AI and machine learning (ML) applications will demand better memory performance and more bits.
- Equipment makers will also benefit from the strength in semiconductor demand driven by AI-related workloads.