Important Information
Investors should not base investment decisions on this website alone. Please refer to the Prospectus for details including product features and the risk factors. Investment involves risks. Past performance is not indicative of future performance. There is no guarantee of the repayment of the principal. Investors should note:
- The investment objective of Global X S&P 500 Covered Call Active ETF (the “Fund”) is to generate income by primarily (i) investing in constituent equity securities in the S&P 500 Index (the “Reference Index”); and (ii) selling (i.e. “writing”) call options on the Reference Index to receive payments of money from the purchaser of call options (i.e. “premium”).
- If the value of the securities relating to the Reference Index held by the Fund declines, the premium that the Fund received for writing the Reference Index Call Option may reduce such loss to some extent. However, the downside of adopting a covered call strategy is that the Fund’s opportunity to profit from an increase in the level of the Reference Index is limited to the strike price of the Reference Index Call Options written, plus the premium received.
- The market value of an Reference Index Call Option may be affected by factors including supply and demand, interest rates. The Fund’s ability to utilise Reference Index Call Options successfully will depend on the ability of the Manager to correctly predict future price fluctuations. If an Reference Index Call Option expires and if there is a decline in the market value of the Reference Index during the option period, the premiums received by the Fund from writing the Reference Index Call Options may not be sufficient to offset the loss realised.
- The Reference Index Call Options in the OTC markets may not be as liquid as exchange-listed options. The Fund may find the terms of counterparties in the OTC markets to be less favorable than the terms available for listed options. Moreover, the exchange may suspend the trading of options in volatile markets which may cause the Fund unable to write Reference Index Call Options at times.
- The use of futures contracts involves market risk, volatility risk, leverage risk and negative roll yields and “contango” risk.
- Investing in Reference Index Futures and writing Reference Index Call Options generally involve the posting of margin. If the Fund is unable to meet its investment objective as a result of margin requirements imposed by the CME and/or the Fund’s broker, the Fund may experience significant losses.
- The Fund employs an actively managed investment strategy. The Fund may fail to meet its objective as a result of the implementation of investment process which may cause the Fund to underperform as compared to direct investments in the constituent equity securities of the Reference Index.
- The Fund is exposed to concentration risk by tracking the performance of securities in a specific regions or countries.
- To the extent that the constituent securities of Reference Index are concentrated in securities of a particular sector or market, the investments of it may be similarly concentrated.
- The trading price of the Fund’s unit on the SEHK is driven by secondary market trading factors, which may lead to a substantial premium or discount to the Fund’s net asset value.
- The Manager may at its discretion pay dividends out of the capital of the Fund. Distributions paid out of capital, represent a return of an investor’s original investment or its gains and may potentially reduce the Fund’s Net Asset Value per Share as well as the capital available for future investment.
- The Fund may suffer from a losses or delays when recovering the securities lent out. This may potentially affect its ability to meet payment and redemption obligations. Collateral shortfalls due to inaccurate pricing or change of value of securities lent, may cause significant losses to the Fund.
Product Introduction
Global X S&P 500 Covered Call Active ETF (3415)
Index yield is not equivalent to yield/return of the fund. Positive yield does not mean positive return. Covered call writing can limit the upside potential of the underlying security. Payments of distributions out of capital or effectively out of capital amounts to a return or withdrawal of part of an investor’s original investment or from any capital gains attributable to that original investment. Any such distributions may result in an immediate reduction in the Net Asset Value per Share of the Fund and will reduce the capital available for future investment.
Investment Points
- Tax Efficiency for HK Investors: Unlike US-listed counterparts, HK-listed ETFs are not subject to dividend withholding tax, enhancing net yields for local investors.
- Innovative Income Strategy: The ETF aims to deliver monthly distributions (not guaranteed and may be paid from capital)*, providing investors with an appealing income stream.
- Downside Cushioning: By writing call options on the S&P 500 index, the strategy generates option premium income, which provide downside protection during market declines.
Global X S&P 500 Covered Call Active ETF (3415) seeks to generate income by primarily (i) investing in constituent equity securities in the S&P 500 Index; and (ii) selling call options on the S&P 500 Index to receive option premium.
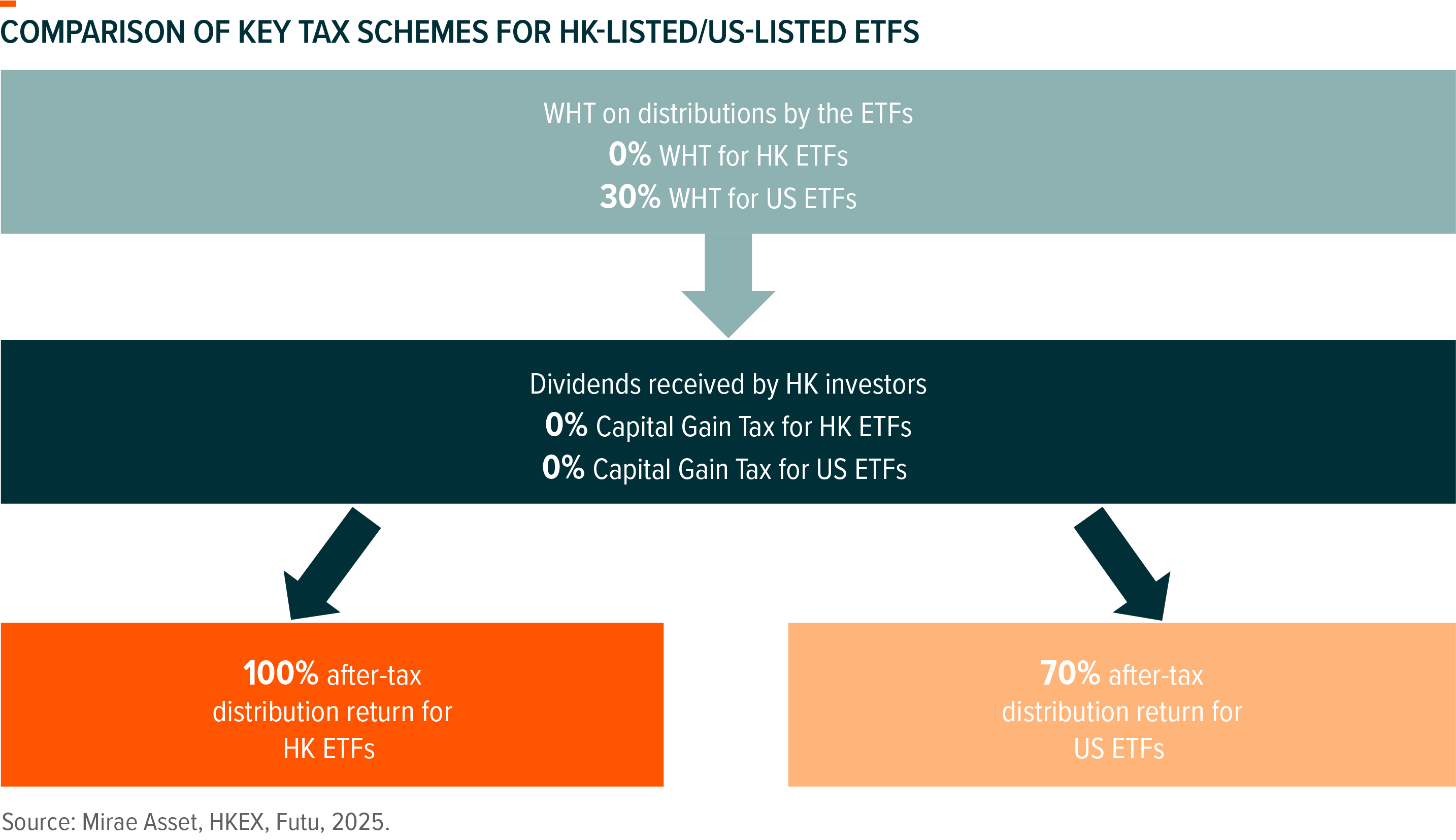
HK Listed ETFs Offer Tax Advantage vs US Listed Counterparts
For Hong Kong investors, HK-listed ETFs carry a significant tax advantage on dividends compared to their US-listed counterparts. As non-US tax residents, Hong Kong investors are subject to a 30% US withholding tax (WHT) on cash dividends distributed by US stocks and ETFs. While partial recovery of this tax may be possible through specific procedures and applications, the process is often complex. Additionally, Hong Kong investors face no capital gains tax on either US or HK-listed ETFs. Consequently, the after-tax return from distributions is 100% for Hong Kong-listed ETFs but only 70% for US-listed ETFs after the standard withholding tax deduction.
What is Covered Call Strategy?
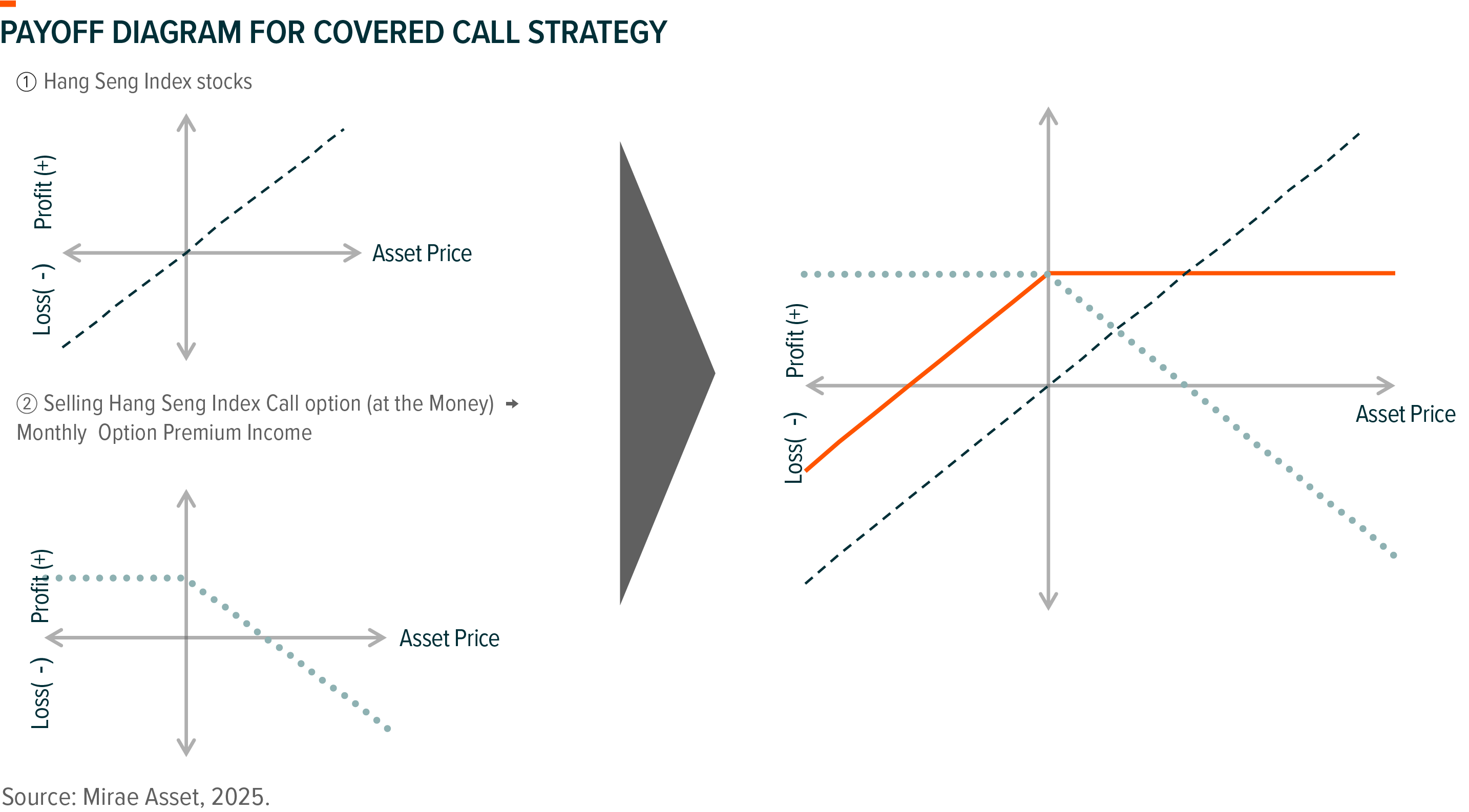
Covered call is an option strategy in which an investor holds certain stocks (or indexes), while at the same time sells a call option (the right for investors to buy stocks at pre-determined prices within a specific timeframe) on the stocks they already own.
Below chart shows the payoff diagram for covered call strategy. It contains two parts: (1) By holding underlying asset (Hang Seng Index for example), investors receive positive returns when asset price goes up, and negative returns when asset price goes down; (2) By selling respective call options, Investors can receive option premiums income. However, when asset price goes up, investors that sell call option will incur losses when the option gets exercised. Through combination of (1) and (2), the orange line in the chart below represents the payoff for Covered Call Strategy.
Features of Covered Call Strategy
Through selling call option, investors can receive option premiums as income. Option premiums tend to increase during volatile markets, offering a potential risk management component.
However, upside potential for covered call is capped in the event that the stock appreciates beyond the strike price. In other words, investors cannot enjoy the benefits of capital appreciation of underlying stocks.
When share price decreases, option premiums offer additional layer of protection that can partially offset losses. No additional downside protection beyond the premiums received.
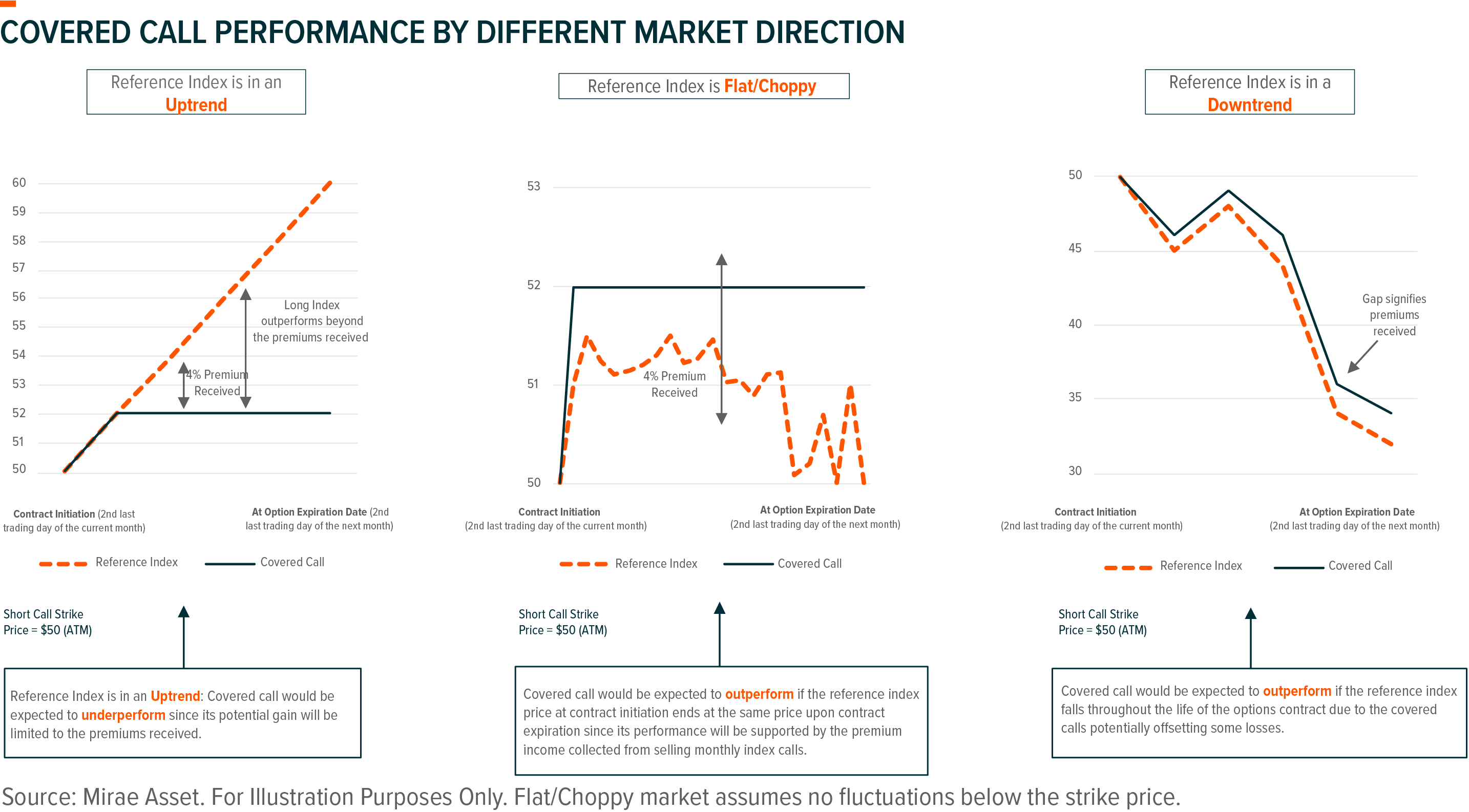
Consider three different market conditions:
-
When market is in an uptrend, reference index/stock goes up
In this case, the major source of income for covered call investors will still be option premiums income from selling call options. In other words, investors cannot enjoy capital appreciation in a bull market. As a result, covered call strategy is likely to underperform underlying indexes/stocks in this market condition.
-
When market is volatile, reference index/stock is flat/choppy
In this case, investors are likely to receive higher option premiums income, as option premiums tend to increase along with market volatility. Covered call strategy would be expected to outperform underlying indexes/stocks in a volatile market.
-
When market is in a downtrend, reference index/stock goes down
In this case, option premiums received can partially offset the loss of underlying indexes/stocks, leading to outperformance against underlying. However, this does not mean that covered call strategy can eliminate loss scenarios for investors, as downside protection cannot go beyond option premiums collected.
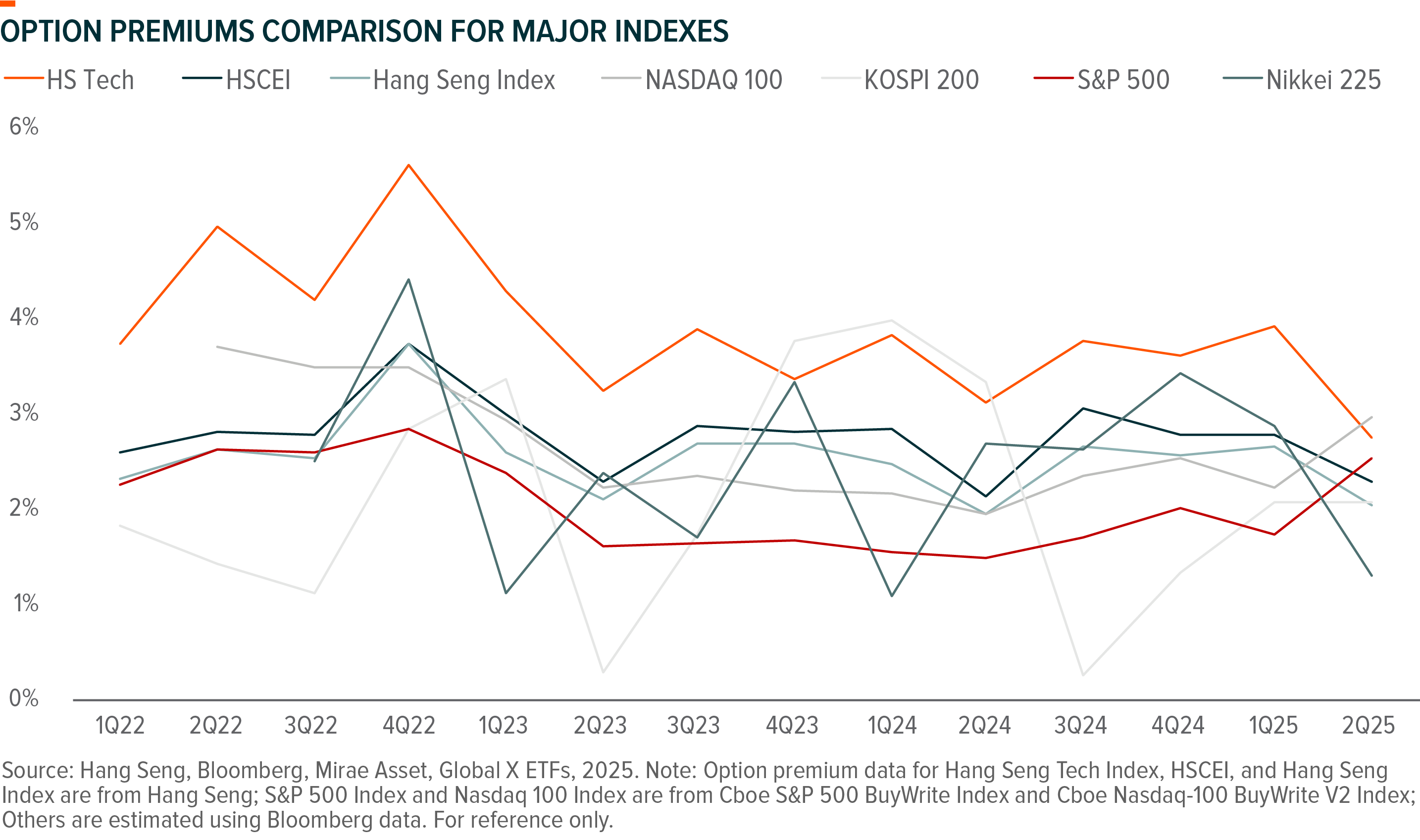
Option Premiums Comparison for Major Indexes
S&P 500 index delivered 1.9% average premium over the past 5 years, relatively lower than Nasdaq 100 – a higher growth, higher volatility index dominated by tech companies.
Covered Call ETF: Streamlined Access to the Strategy
Covered call strategy is an effective income-generating strategy for investors to navigate market uncertainty. However, it could be costly and time consuming for non-professional investors to adopt such strategy as it involves options trading. In this case, covered call ETF stands out as a more suitable option because of its low costs, ease of trading, and transparency.
Risks
Option premium can partially offset losses in market downturn, but it does not mean that investors will not lose money when market goes down. The protection from covered call strategy does not go beyond option premium, and Investors may still incur losses in when underlying indexes/stocks decline.
Upside return potential is capped for covered call strategy. When market goes up, the return for investors does not go beyond option premiums received, thus investors cannot enjoy the capital appreciation of its underlying indexes/stocks.